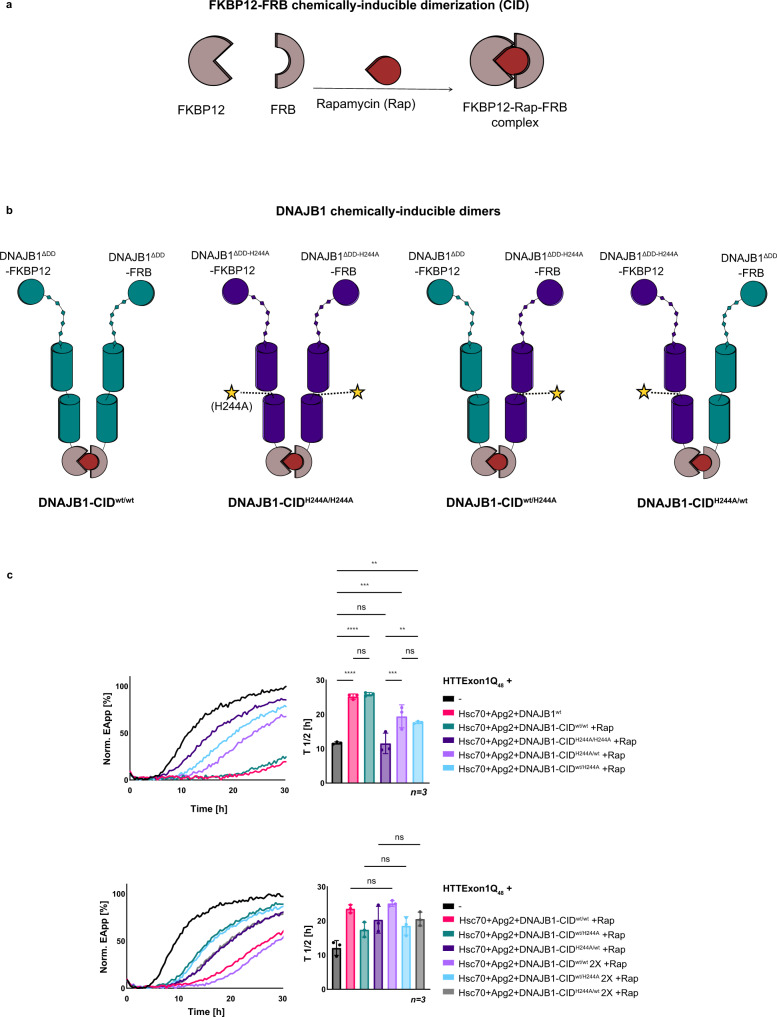
Fig. 5. Protomers of DNAJB1 act independently in the suppression of HTTExon1Q48 aggregation with Hsc70 and Apg2.
a Schematic representation of a chemically induced dimerization (CID) system. FKBP12 and FRB heterodimerize upon the addition of Rapamycin. b Schematic representation of DNAJB1 chemically induced dimers. DNAJB1ΔDD (teal) and DNAJB1ΔDD-H244A (dark purple) were expressed as fusion constructs with either FKBP12 or FRB. The addition of Rapamycin facilitates dimer formation of DNAJB1-CIDwt/wt (teal), DNAJB1-CIDH244A/H244A (dark purple), DNAJB1-CIDwt/H244A (mixed protomers) and DNAJB1-CIDH244A/wt (mixed protomers). c Top, FRET analysis of HTTExon1Q48 aggregation upon addition of Hsc70, Apg2, and DNAJB1wt or DNAJB1-CIDs in the presence of Rapamycin (Rap): DNAJB1-CIDwt/wt (teal), DNAJB1-CIDH244A/H244A (dark purple), DNAJB1-CIDwt/H244A (light blue), DNAJB1-CIDH244A/wt (light purple). Bottom, FRET analysis of HTTExon1Q48 aggregation upon addition of single or double the concentration (2x) of DNAJB1-CIDs in the presence of Rap: DNAJB1-CIDwt/wt (magenta and light purple), DNAJB1-CIDwt/H244A (teal and light blue), DNAJB1-CIDH244A/wt (dark purple and gray).The graphs are a representative result of three independent experiments and a one-way ANOVA analysis of the half-life (T1/2) of HTTExon1Q48 aggregation under the tested conditions is depicted on the right. Bars represent the mean value and error bars correspond to the mean SD. ****P ≤ 0.0001; ***P ≤ 0.001; **P ≤ 0.01; ns not significant.