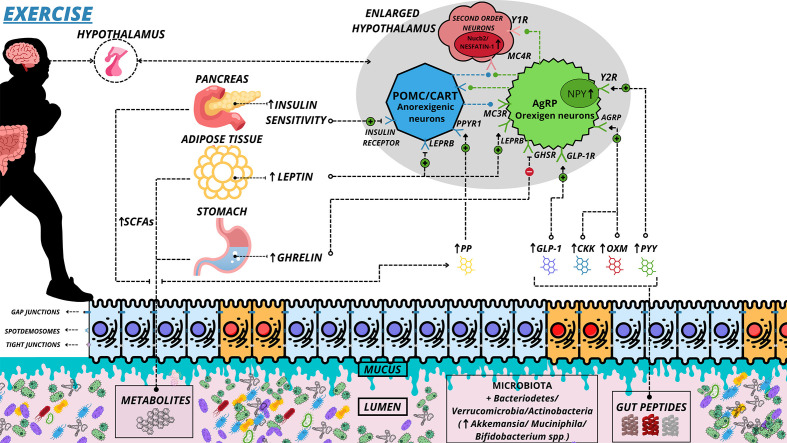
Figure 3.
Alteration of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in exercise. Main hormonal changes in response to physical exercise. Exercise can maintain the health of epithelial cells, and cell communications remain healthy, without permeability of substances to systemic circulation. Mucus preservation and improved interaction of peptides/hormones with their receptors also occur, creating optimal conditions. Blue cells represent healthy. (↑) Increase Secretion and Greater; (↓) Decrease Secretion and Decline; (⊕) Positive interaction; (⊖) Negative Interaction; (⊘) Non Interaction; SCFAs, Short-Chain Fatty Acid; PYY, Peptide YY; OXM, Oxytomodulin; PPYR1, Pancreatic Polypeptide Receptor 1; PP, Pancreatic Polypeptide; GLP-1, Glucagon Like Peptide-1; GLP-1R, Glucagon Like Peptide-1 Receptor; LEPRB, Leptin Receptor Long Isoform; Y1R, Neuropeptide Y Receptor type 1; Y2R, - Neuropeptide Y Receptor type 2; GHSR, - Growth Hormone Secretagogue receptor; CKK, Cholecystokinin; MC3R, Melanocortin 3 Receptor; MC4R, Melanocortin 4 Receptor; AgRP, Agouti-Related Protein.