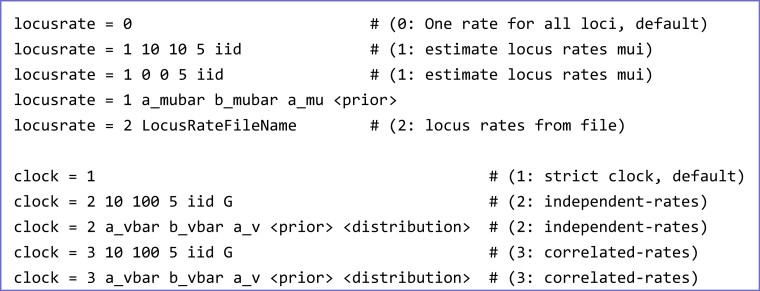
Fig. 2.
The relaxed-clock models are specified using two control variables in bpp: (i) locusrate concerning the overall rate for locus and (ii) clock concerning the rate variance parameter for locus . The locusrate variable is used with any of the three clock models (clocks 1, 2, 3). In the example and specify the mean overall rate . When there are no fossil calibrations on the species tree, is fixed, specified using . Given the mean overall rate , the overall rates for loci () are generated from the conditional-independence model (iid) or the gamma-Dirichlet model (dir), with the shape parameter ( 5 in the example) specifying how similar are among loci. The clock variable specifies the three clock models: clock 1 (strict clock), clock 2 (independent-rates model), and clock 3 (correlated-rates model). Under both clock 2 and clock 3, the average rate variance parameter is specified as ; in the example and with mean 0.1. Given , the variance for locus is similarly generated from the iid or dir models. Given the overall rate and the rate variance parameter for locus , rates for branches at locus are specified for clock 2 and clock 3 using either the gamma (G) or log-normal (LN) distributions.