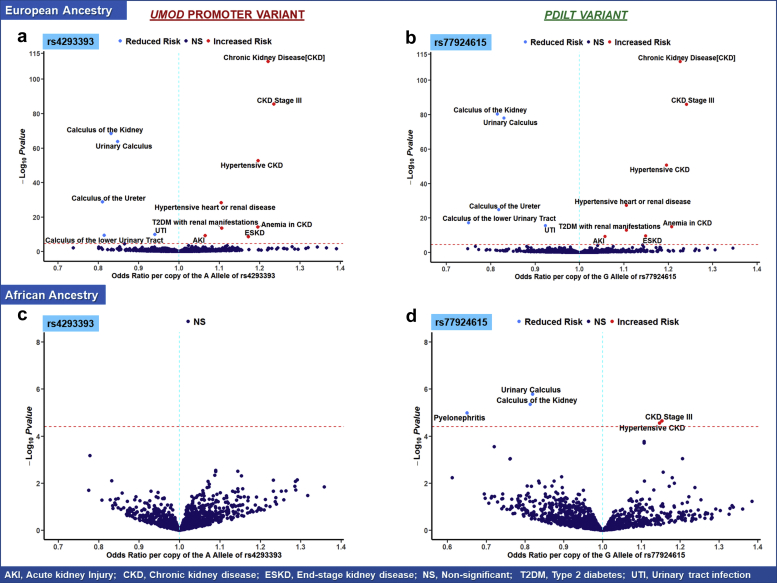
Figure 2.
Volcano plot illustrating key clinical phenotypes significantly associated with UMOD promoter (rs4293393) and PDILT variants (rs77924615) in (a, b) non-Hispanic White and (c, d) non-Hispanic Black patients in the Million Veteran Program. In each plot, the red line indicates the significance threshold for Bonferroni correction as a reference. Phenotypes in the right upper quadrant have increased odds per copy of the allele associated with increased Umod expression, whereas phenotypes in the left quadrant have decreased odds. In Black patients, no significant variant-phenotype associations were observed for the rs4293393 UMOD promoter variant. Five significant variant-phenotype associations were observed for the PDILT variant rs4293393. In White patients, a wide range of significant variant-phenotype associations were observed corroborating the pleiotropic effects of Umod on human physiology. In addition, there were no noticeable differences in the patterns of variant-phenotype associations between UMOD promoter and PDILT variants. AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; ESKD, end-stage kidney disease; NS, nonsignificant; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; UTI, urinary tract infection.