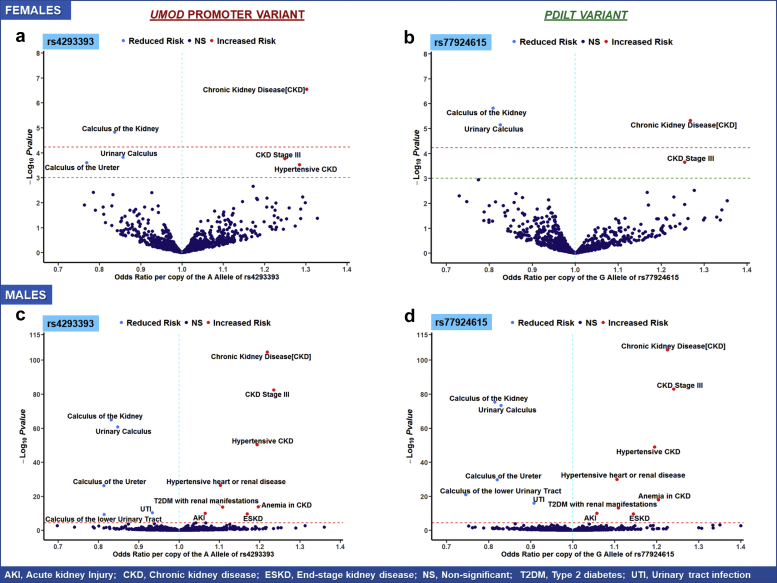
Figure 3.
Volcano plot illustrating key clinical phenotypes significantly associated with UMOD promoter (rs4293393) and PDILT variants (rs77924615) in non-Hispanic White female (a, b) and male (c, d) patients in the Million Veteran Program. In each plot, the red line indicates the significance threshold for Bonferroni correction as a reference whereas the green line indicates nominal significance at α = 5 × 10−3. Phenotypes in the right upper quadrant have increased odds per copy of the allele associated with increased Umod expression, whereas phenotypes in the left quadrant have decreased odds. All clinical phenotypes typically associated with Umod expression had significant associations with UMOD promoter and PDILT variants in White male patients. In White female patients, significant variant-phenotype associations were observed for CKD, urinary calculus, and calculus of the kidney. Nominally significant associations were observed with acute cystitis and heart failure with preserved EF. AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; EF, ejection fraction; ESKD, end-stage kidney disease; NS, nonsignificant; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; UTI, urinary tract infection.