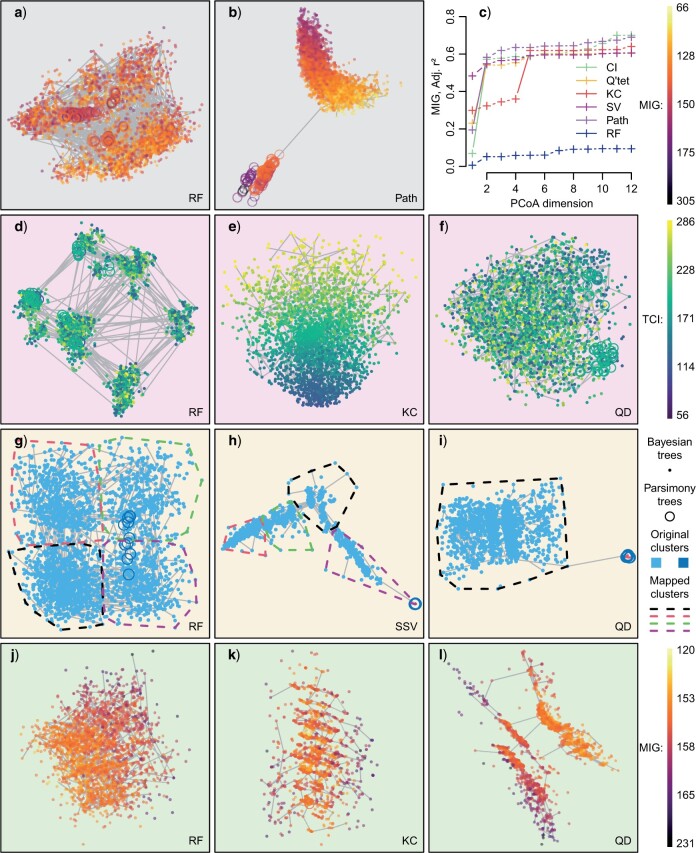
Figure 1.
Different distances can impose tree spaces with different characteristics. First two dimensions of PCoA mappings of tree spaces, with minimum spanning tree of 350 points (solid lines). Higher dimensions depicted in Supplementary Information available on Dryad (Smith 2021). a, b) 2500 Bayesian (dots) and 100 parsimony (rings) trees from analysis of Yates (2003), colored by stratigraphic congruence (MIG, millions of years); (a) RF tree space does not exhibit clear structure; MST indicates that the two apparent clusters do not correspond to clusters in the original tree space, and that the mapping is highly distorted (MST extension factor 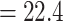 ); (b) path distance tree space (MST extension factor
); (b) path distance tree space (MST extension factor 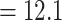 ), showing stratigraphic structure and clear separation of parsimony and Bayesian trees; (c) cumulative correlation of stratigraphic fit (MIG) with first
), showing stratigraphic structure and clear separation of parsimony and Bayesian trees; (c) cumulative correlation of stratigraphic fit (MIG) with first 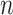 tree space axes; (d–f) 2500 Bayesian and 54 parsimony trees from analysis of Carpenter (2001); points colored by tree balance (TCI; dark
tree space axes; (d–f) 2500 Bayesian and 54 parsimony trees from analysis of Carpenter (2001); points colored by tree balance (TCI; dark  balanced): (d) strong clustering in RF mapping (silhouette coefficient
balanced): (d) strong clustering in RF mapping (silhouette coefficient 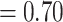 ) has no underlying basis (silhouette coefficient
) has no underlying basis (silhouette coefficient 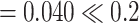 ), as suggested by tortuous minimum spanning tree (extension factor
), as suggested by tortuous minimum spanning tree (extension factor 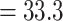 ); (e) vertical axis in KC mapping (MST extension factor
); (e) vertical axis in KC mapping (MST extension factor 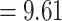 ) shows clear correspondence with tree balance; (f) quartet mapping (MST extension factor
) shows clear correspondence with tree balance; (f) quartet mapping (MST extension factor 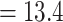 ) faithfully represents the absence of clustering and tree balance correlation present in the original space; (g–i) trees from analysis of Fischer et al. (2016), showing (lack of) correspondence between original clusters (point color, corresponding to Bayesian vs. parsimony trees) and clusters identified from mappings (using hierarchical clustering; dashed lines
) faithfully represents the absence of clustering and tree balance correlation present in the original space; (g–i) trees from analysis of Fischer et al. (2016), showing (lack of) correspondence between original clusters (point color, corresponding to Bayesian vs. parsimony trees) and clusters identified from mappings (using hierarchical clustering; dashed lines  convex hulls); (j–l) trees from analysis of Schoch and Milner (2008), colored by stratigraphic fit; different metrics result in spaces with different (non-clustering) structures, whose validity is supported by inspection of MST and of higher dimensions. CID
convex hulls); (j–l) trees from analysis of Schoch and Milner (2008), colored by stratigraphic fit; different metrics result in spaces with different (non-clustering) structures, whose validity is supported by inspection of MST and of higher dimensions. CID  clustering information distance tree space; KC
clustering information distance tree space; KC  Kendall–Colijn tree space; MIG
Kendall–Colijn tree space; MIG  Minimum implied gap; Q’tet
Minimum implied gap; Q’tet  Quartet tree space; RF
Quartet tree space; RF  Robinson–Foulds tree space; SV
Robinson–Foulds tree space; SV  split size vector tree space; TCI
split size vector tree space; TCI  total cophenetic index.
total cophenetic index.