Table 1.
Performance of selected tree distance metrics against tests of tree distance behavior
| Ranking | Best | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Worst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of move: mis-orderings (0–545) | RF (0) | CID (8) | QD (94) | Path (126) | SV (188) | KC (360) |
| No. leaves moved: inconsistent cases (0–289) |
 CID (0)
CID (0) |
 Path (0)
Path (0) |
SV (2) | KC (11) | QD (17) | RF (289) |
| Saturation: 11-leaf trees with max score (1–100,000) |
 CID (1)
CID (1) |
 QD (1)
QD (1) |
 Path (1)
Path (1) |
 SV (1)
SV (1) |
KC (3) | RF (86,336) |
| Sensitivity: distinct values (100,000–1) | CID (28,939) | KC (581) | SV (541) | Path (302) | QD (200) | RF (6) |
Shape independence: 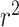 (0–1) (0–1) |
QD (10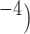
|
CID (0.0079) | RF (0.024) | SV (0.055) | KC (0.35) | Path (0.48) |
Balance independence: 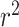 (0–1) (0–1) |
RF (0.0001) | QD (0.0007) | CID (0.0014) | SV (0.004) | Path (0.027) | KC (0.375) |
| Cluster recovery: mean rank (1–25) | CID (7.2) | QD (9.8) | RF (10.9) | KC (14.1) | Path (16.3) | SV (16.9) |
| Bullseye subsampling successes (1000–0) | CID (650) | Path (633) | QD (626) | SV (588) | KC (573) | RF (410) |
| Bullseye miscoding successes (1000–0) | CID (941) | QD (809) | RF (781) | SV (709) | Path (704) | KC (598) |
SPR rearrangement: Kendall’s 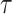 (1–0) (1–0) |
CID (0.771) | RF (0.744) | QD (0.739) | SV (0.608) | Path (0.536) | KC (0.482) |
Random distances interquartile range ( of median) of median) |
QD (1.6) | CID (1.6) | SV (2.2) | Path (18.8) | KC (35.2) | RF (n/a*) |
Note: Parentheses denote range of possible scores for each measure (best to worst). Note that random tree pairs obtain the maximum possible RF distance, resulting in a zero interquartile range (*). Full details and results in Smith (2020a) and Smith (2021).
CID  clustering information distance; KC
clustering information distance; KC  Kendall–Colijn distance; QD
Kendall–Colijn distance; QD  quartet distance; RF
quartet distance; RF  Robinson–Foulds distance; SV
Robinson–Foulds distance; SV  split size vector distance.
split size vector distance.
