Figure 2. Differential Brain Structures Associated With Initiation of Tobacco Use in Childhood.
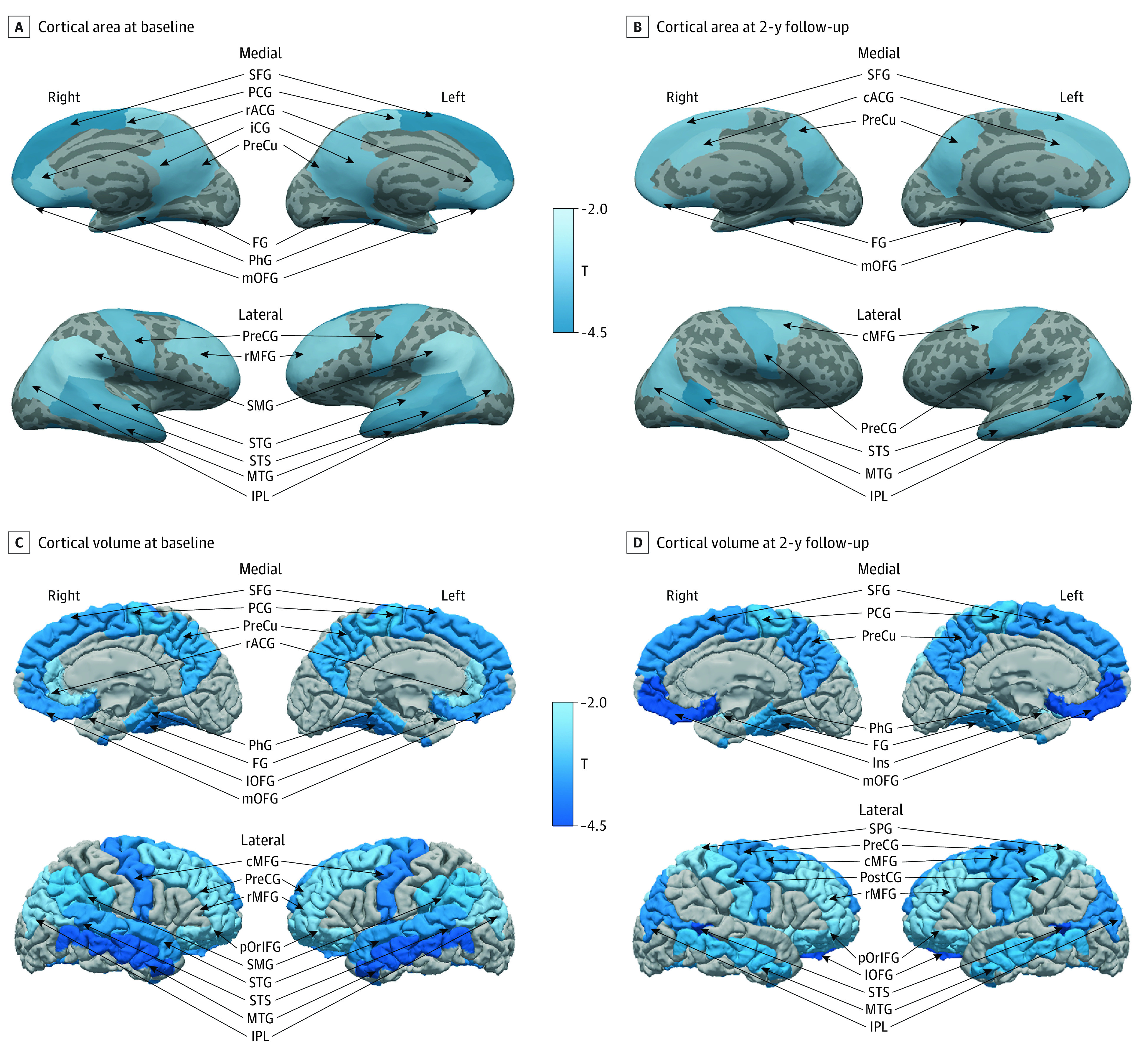
Cortical surface measurements include 15 clusters at baseline and 10 clusters at 2-year follow-up. Cortical volume measurements include 17 clusters at baseline and 2-year follow-up. Brain structures significantly associated with early initiation of tobacco use (false discovery rate <0.05) are labeled by T values of cortical area and volume between ever tobacco users and nonusers, adjusted by age, sex, race and ethnicity, pubertal stage, substance ever use, parental monitoring, school environment, handedness, imaging device manufacturer, and study site. cACG indicates caudal anterior cingulate gyrus; cMFG, caudal middle frontal gyrus; FG, fusiform gyrus; iCG, isthmus cingulate; Ins, insula; lOFG, lateral orbitofrontal gyrus; mOFG, medial orbitofrontal gyrus; MTG, middle temporal gyrus; IPL, inferior parietal lobule; PCG, paracentral gyrus; PhG, parahippocampal gyrus; pOrIFG, pars orbitalis; PostCG, postcentral gyrus; PreCG, precentral gyrus; PreCu, precuneus; rACG, rostral anterior cingulate gyrus; rMFG, rostral middle frontal gyrus; SFG, superior frontal gyrus; SMG, supramarginal gyrus; STG, superior temporal gyrus; and STS, banks of superior temporal sulcus.
