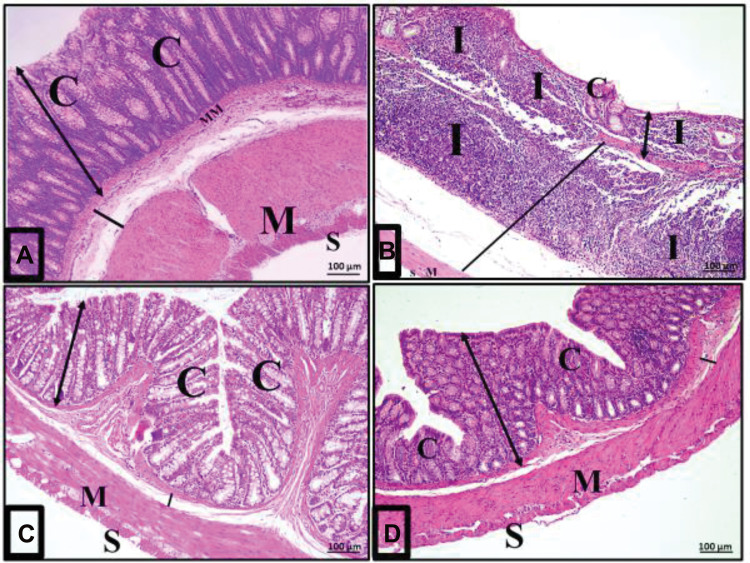
Figure 5.
Acute diclofenac toxicity induced histological changes and damage of the colon layers that were prevented and treated using Ajwa date fruits. (A) Architecture of normal colon histology: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon of group I (control group) showing normal mucosa (double head arrow), submucosa (black line), musculosa (M) and serosa (S). The mucosa is folded, intact, continuous and has close regularly arranged tubular crypts (C) occupying the whole thickness of the mucosa and resting on the muscularis mucosa (MM). (B) Disturbances of colon histological architecture induced by ATD: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from group II (acute diclofenac toxicity group) showing distorted mucosa (double head arrow) with absence of folding, loss of surface columnar epithelial cells and malformed or even absent crypts (C). There was heavy inflammatory infiltration (I) mainly lymphocytes in the lamina propria of the mucosa and in the widened submucosa (black line). (C) Preventive effects induced by ADFE against ATD: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from the toxicity prevention group (group IV) against acute diclofenac toxicity using ADFE showing mostly normal folded mucosa (white line) and regular crypts (C) where the normal submucosa (black line), musculosa (M) and serosa (S) were normal. (D) Therapeutic effects induced by ADFE against ATD: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from group III (toxicity treatment group against acute diclofenac toxicity using ADFE) showing an almost normal histological appearance compared with the control group mucosa (double head arrow), crypt (C), submucosa (black line), musculosa (M) and serosa (S) (H&E, x100).