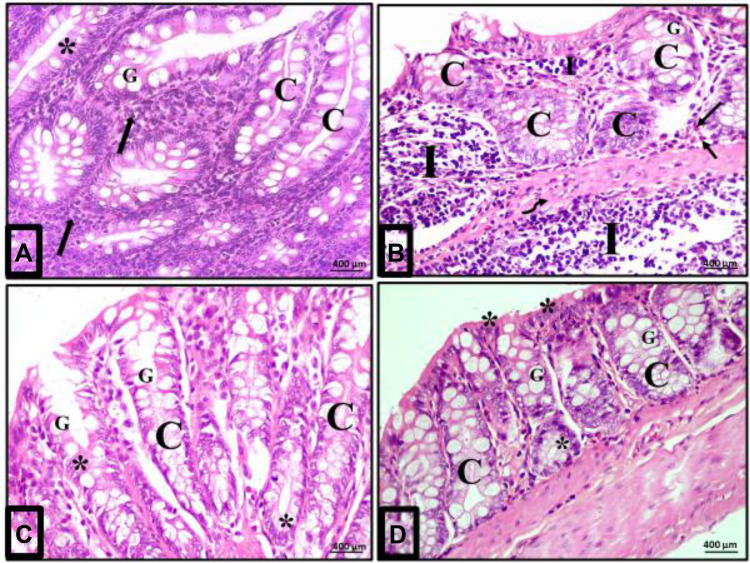
Figure 6.
Acute diclofenac toxicity induced inflammatory effects in colon mucosa that were prevented and treated using Ajwa date fruit extract. (A) Normal cellularity of the colon: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon of group I (control group) showing a normal histological architecture of mucosa of the colon. The crypt (C) is lined mainly by simple columnar absorptive cells (stars) and goblet cells (G). Numerous immune cells mainly lymphocytes are detected in the lamina propria (arrows). (B) Damage of colon cellularity induced by ATD: A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from group II (acute diclofenac toxicity group) showing distorted mucosa with irregular crypts (C) with decreased number of goblet cells (G). N.B: 1-There is a heavy infiltration of the lamina propria and submucosa with inflammatory cells mainly lymphocytes (I) and eosinophils (arrows) in the lamina propria. 2- There is a submucosal exudate (curved arrow). (C) Preventive effects to colon cells induced by ADFE against ATD (group IV): A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from toxicity prevention group (prevention group of acute diclofenac toxicity using ADFE) showing mucosa with preserved crypt architecture (C) lined with simple columnar epithelium (stars) and numerous goblet cells (G). (D) Therapeutic effects to colon cells induced by ADFE against ATD (group III): A photomicrograph of a section in the colon from toxicity treatment group (treatment group of acute diclofenac toxicity using ADFE) showing the crypts (C) lined with simple columnar epithelium (stars) and numerous goblet cells (G). (H&E, x400).