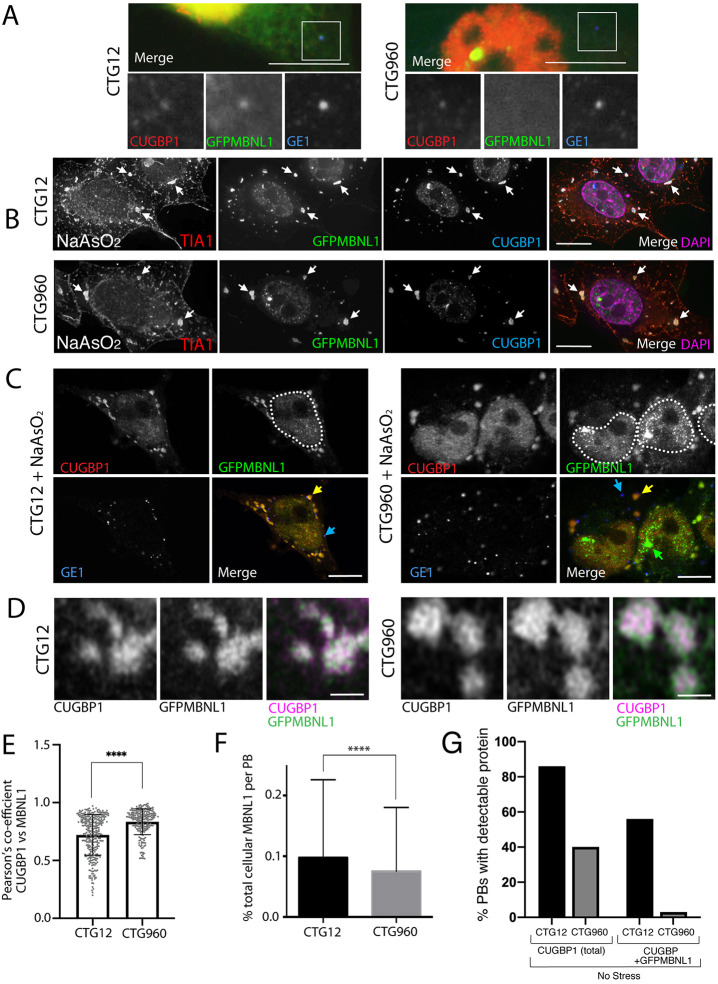
Fig. 4.
MBNL1 and CUGBP1 colocalise in P-bodies and sub-regions of SGs in HeLa models of DM1. (A) Unstressed HeLa_CTG12_GFPMBNL1 (CTG12, left) and HeLa_CTG960_GFPMBNL1 (CTG960, right) stained for CUGBP1 (red), GFP-tagged MBNL1 (GFPMBNL1; green) and GE1 (blue). For CTG12 cells, the merged image (top) shows colocalization of GE1 with CUGBP1 and GFPMBNL1 in cytoplasmic P-bodies. For CTG960 cells, the merged image (top), shows colocalization of GE1 with CUGBP1 in P-bodies, but GFPMBNL1 (green) is not detectable. Magnified images of the boxed P-bodies are shown below. Scale bars: 10 µm. Red and green signals in these images have been adjusted to visualise the cytoplasmic P-bodies, resulting in saturation of the nuclear signal. (B) CTG12 (top) and CTG960 (bottom) cells after treatment with NaAsO2, showing SGs (arrows) containing TIA1 (red in merged image), GFPMBNL1 (green in merged image) and CUGBP1 (blue in merged image). Scale bars: 10 µm. (C) CTG12 (left) and CTG960 (right) cells treated with NaAsO2. SGs (yellow arrows) show colocalisation of CUGBP1 (red in merged images) and GFPMBNL1 (green in merged images). Blue arrows highlight large number of P-bodies (detected with GE1, blue in merged images) also present in both cell lines. Nuclear foci of GFPMBNL1 (green in merged image) are only present in CTG960 cells (green arrow). Dotted lines show the approximate outlines of nuclei by using GFPMBNL1 signal. Scale bars: 10 µm. (D) Super-resolution airyscan images of SGs showing non-uniform distribution of CUGBP1 (magenta in merged images) and GFPMBNL1 (green in merged images) in CTG12 (left) and CTG960 (right) cells. Scale bars: 1 µm. (E) Graph of Pearson correlation coefficient of colocalisation between CUGBP1 and GFPMBNL1 in SGs of CTG12 and CTG960 cells (****P<0.00001; n=204 SGs and n=229 SGs in CTG960 and CTG12 cells, respectively, from three independent experiments; unpaired t-test). (F) Analysis of the amount of GFPMBNL1 in the P-bodies of CTG12 and CTG960 cells that had been treated with NaAsO2. The percentage of GFPMBNL1 in P-bodies of CTG960 cells (n=670 P-bodies from 53 cells) was reduced compared with that in P-bodies of CTG12 cells (n=924 P-bodies from 34 cells); ****P<0.0001 unpaired t-test). (G) Unstressed CTG960 and CTG12 cells were induced with doxycycline for 72 h. P-bodies (in %) that contain CUGBP1 or CUGBP1 plus MBNL1 are reduced in CTG960 cells compared with levels in CTG12 cells (n=100 cells per cell line per experiment). All data are displayed as the mean±s.d. (see also Fig. S5).