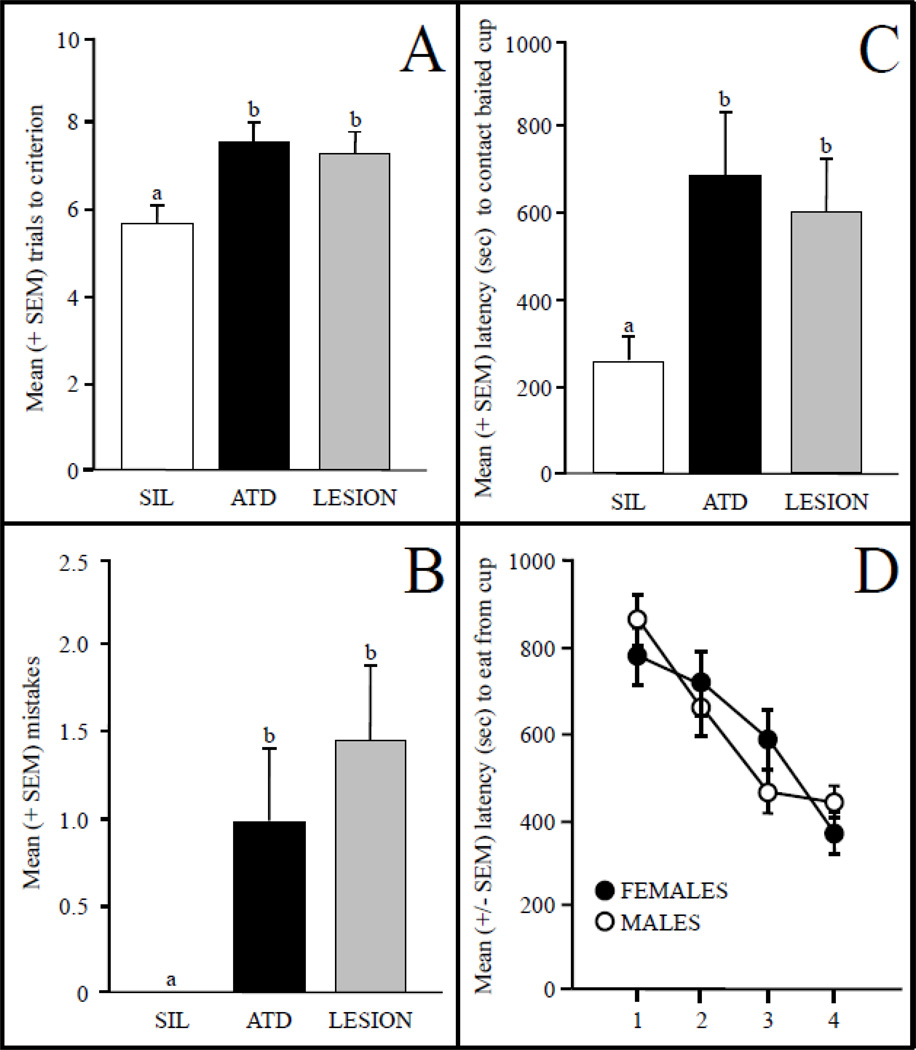
Figure 2.
Number of trials to reach criterion in birds whose hippocampus (HP) was treated with silicone (SIL) pellets as a control, the aromatase inhibitor ATD, or in which lesions were produced with an excitotoxin (panel A). In panel B, the average numbers of mistakes made by birds in the first probe trial are indicated, and their latencies to reach the baited cup in that trial are displayed in panel C. Inhibition of aromatase in the HP significantly increased the number of learning trials as well as mistakes prior to contacting and latencies to reach the learned cup relative to the control group. Interestingly, performance by ATD birds was statistically indistinguishable from birds with lesions of the HP. In a separate study, male and female zebra finches did not differ in acquisition rate in this task (data not shown), but the latencies of male birds decreased at a significantly faster rate than those of females over the probe trials (panel D). Data from Bailey et al. (2009, 2013).