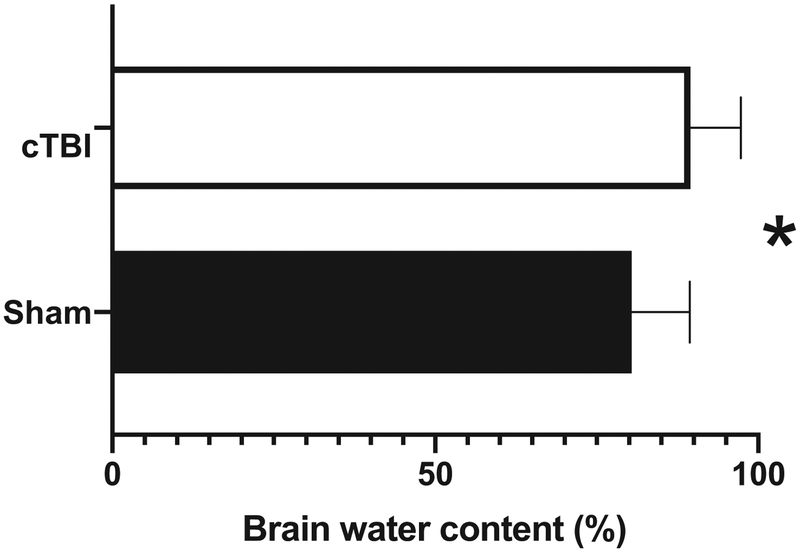
Figure 2.
A single concussive injury was directed to the brain of an anesthetized adult zebra finches as described in Figure 1. 6 hours following injury, a 4mm diameter brain sample was collected and immediately weighed for the wet weight (WW). Brain samples were then placed at 110C for 24 hours and weighed again for the dry weight (DW). Brain water content or edema was calculated as %H2O = (WW - DW) × 100/WW. Edema (as measured by brain water content) is significantly higher in birds that underwent concussive traumatic brain injury (cTBI) relative to shams as measured using a one tailed Mann-Whitney U. * denotes a significant difference at P <0.05