Figure 2. Distributed motor network for reach to grasp control and stroke syndromes.
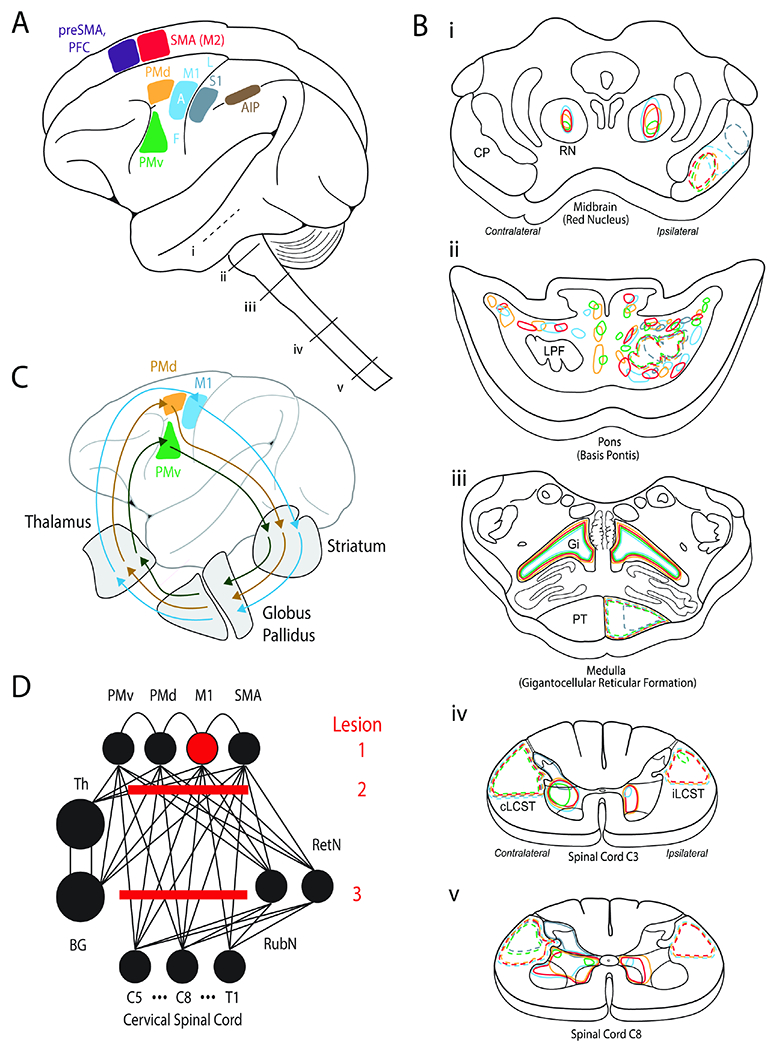
A. Cortical areas implicated in motor control. SMA=supplementary motor area or secondary motor area (M2). PFC=prefrontal cortex. PMd=dorsal premotor cortex. PMv=ventral premotor cortex.
M1=primary motor cortex. S1=primary somatosensory cortex. AIP=anterior inferior parietal. F=face. A=arm. L=leg. i-v show segments of the brainstem and spinal cord that are then illustrated in (B).
B. Expanded view of i-v segments from A. The color coding illustrates projections from cortical motor areas to each of the segments as delineated by tracer studies.
C. Parallel recurrent pathways between premotor and motor cortices to the basal ganglia and thalamus.
D. Highly connected neural network for motor control. Lesion 1 represents an isolated ‘hand knob’ cortical M1 stroke. Lesion 2 is in the corona radiata (“subcortical”), which is more common. Lesion 3 is also a common lesion in the brainstem.
