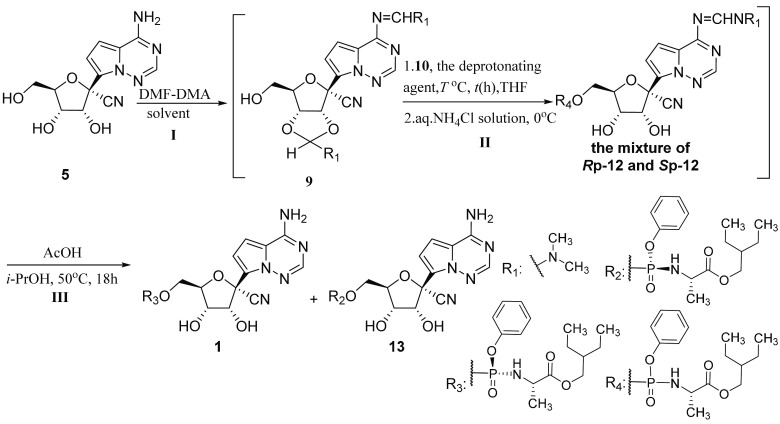
Table 1. Condition Optimization of the Condensation Reaction (I) and the Phosphorylation Reaction (II)a.
|
I |
II |
III |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | solvent | pyridine (equiv.) | deprotonating agent | T (°C) | T (h) | LCAP of 1 (%)d | d.r. ratioe (1/13) |
| 1 | pyridineb | MeMgCl | –10 | 2 | 96.7 | 161/1 | |
| 2 | THFc | MeMgCl | –10 | 2 | 93.0 | 36/1 | |
| 3 | THFc | 1.0 | MeMgCl | –10 | 2 | 92.7 | 42/1 |
| 4 | pyridineb | MeMgCl | –20 | 2 | 92.9 | 232/1 | |
| 5 | pyridineb | t-BuMgCl | –20 | 2 | 94.1 | 783/1 | |
General procedure: the condensation reaction of compound 5 (500 mg, 1.72 mmol, 1 equiv.) and DMF-DMA (820 mg, 6.88 mmol, 4.0 equiv.) afforded compound 9. The coupling of the obtained crude 9 and compound 10 (1.02 g, 2.06 mmol, 1.2 equiv.) was performed in the presence of the deprotonating agent (2.58 mmol, 1.5 equiv.). When crude 9 disappeared, the phosphorylation was quenched with aq. NH4Cl solution and provided compound 12. After simple aftertreatment, crude 12 was subjected to the solution of acetic acid (2.06 g, 34.4 mmol, 20.0 equiv.). Finally, product 1 was obtained.
The condensation was conducted at 25 °C for 3 h.
The condensation was conducted at 60 °C for 3 h.
LCAP: the area (%) of compound 1 determined by HPLC in the final reaction mixture.
The d.r. ratio was determined by HPLC.