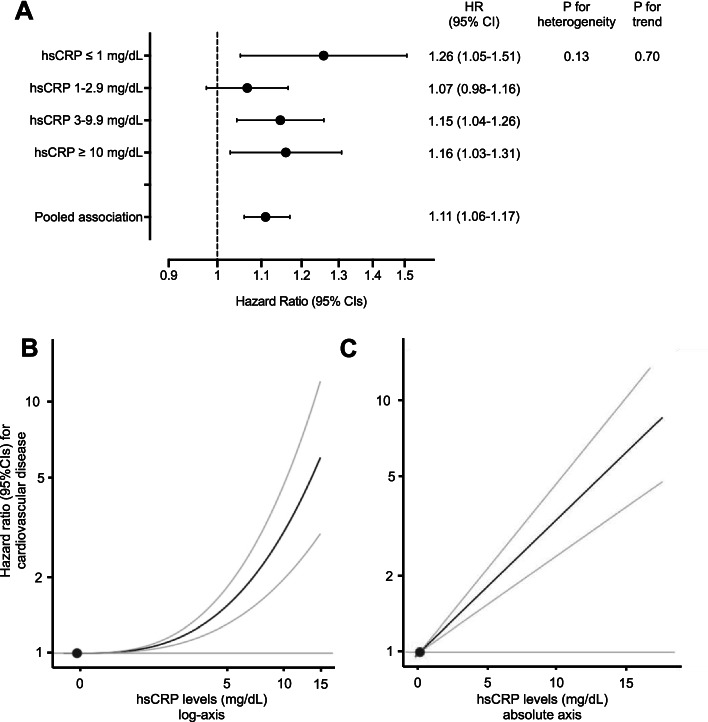
Fig. 1.
Associations between genetically predicted IL-6R-mediated signaling and risk of incident cardiovascular disease across measured hsCRP levels. A Mendelian randomization analyses stratified by baseline hsCRP levels. The hazard ratios are scaled for 1 mg/dL increment in absolute hsCRP levels. The p-values for heterogeneity and for trend are derived from the Cochran Q statistic and linear meta-regression analyses across deciles of measured hsCRP. B, C Mendelian randomization analyses of genetically predicted IL6R-mediated signaling and CVD risk across B ln-transformed measured hsCRP levels and C absolute measured hsCRP levels. For B, C, results are obtained from fractional polynomial models across associations derived for deciles of measured hsCRP levels. The reference is set to the minimum hsCRP value in the UK Biobank sample (0.08 mg/dL). The p-values for non-linearity are 0.001 for ln-transformed hsCRP levels and 0.99 for absolute hsCRP levels. For all graphs, the residual values of hsCRP are used to stratify, as determined in models regressing the genetic risk score for IL-6 signaling on measured hsCRP levels