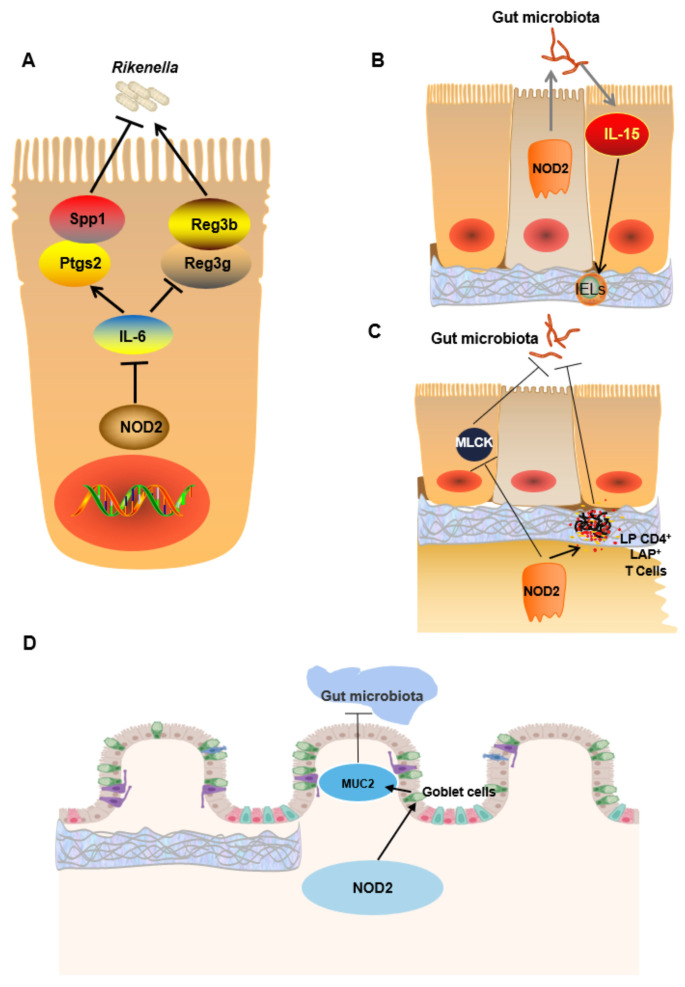
Figure 1.
Nod2 mediated regulation of gut microbiota. (A) Nod2 in epithelial cells inhibits the expression of IL-6 and subsequently Ptgs2 and Spp1, and increases the expression of Reg3β and Reg3γ, thus increasing the abundance of Rikenella. (B) Nod2 maintains IELs via recognition of gut microbiota. The loss of IELs in Nod2−/− mice is caused by the impaired expression of IL-15. (C) Nod2 can inhibit the overexpression of MLCK, avoiding the opening of tight junctions of epithelial cells, decreasing permeability of intestinal epithelial mucosa and bacterial translocation. Nod2 can also affect the number of LP CD4+LAP+ T cells, and regulate gut microbiota and improve colitis. (D) Nod2 can promote the secretion of Muc2 by intestinal goblet cells and enhances intestinal barrier function, thereby limiting bacterial displacement.