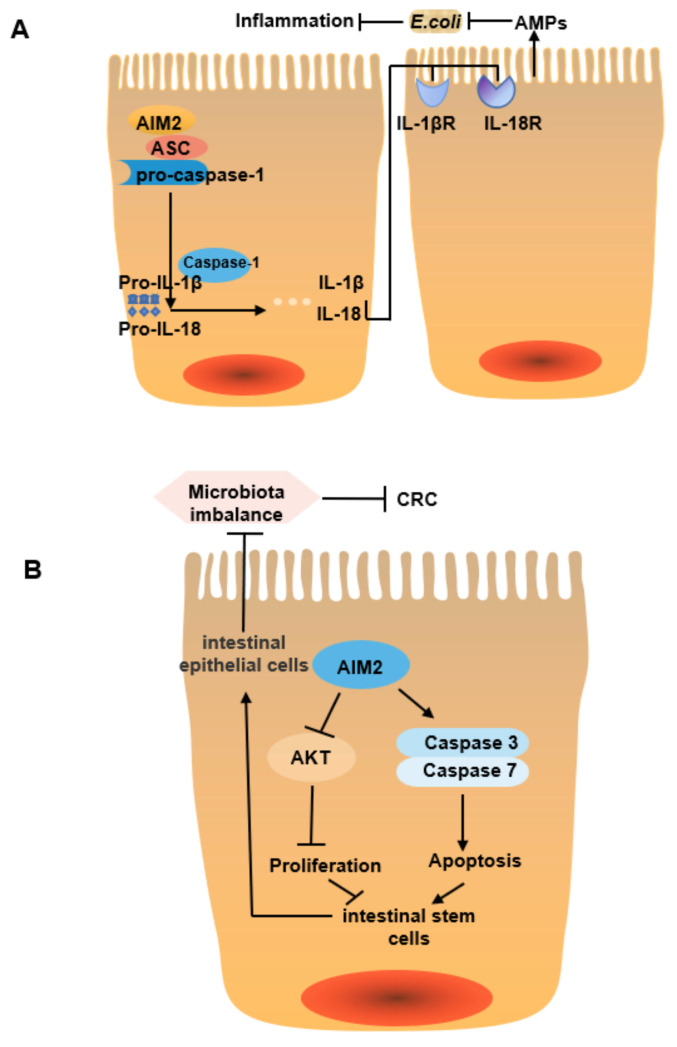
Figure 2.
The pathway for Aim2 mediated regulation of microbiota. (A) Aim2 in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) is activated by microbiota dsDNA in the cytoplasm and assembles the inflammasome by recruiting ASC and pro-caspase-1. The Aim2 inflammasome activates caspase-1 and induces the maturation of IL-1β and IL-18, which bind to their respective receptors IL-1βR and IL-18R on epithelial and immune cells, thereby increasing the production of AMPs to inhibit E. coli and reducing host susceptibility to colitis. (B) Aim2 can inhibit AKT and activate caspase3/7 signaling pathway to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis, thus preventing intestinal stem cells from overproliferating and thus differentiating to form mature intestinal epithelial cells, thereby inhibiting gut microbiota translocation disorder and tumorigenesis.