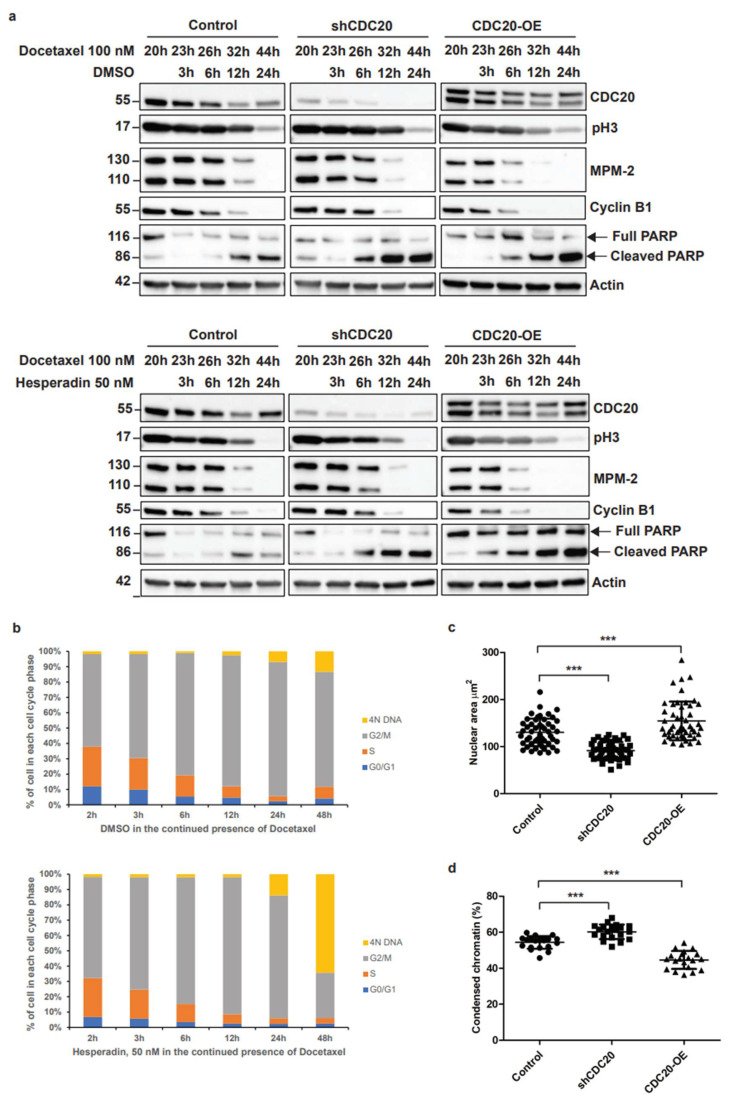
Figure 2.
Elevated CDC20 is correlated with mitotic slippage, a possible reason causing an increase in nuclear size and chromatin decondensation in cancer cells. (a) MDA-MB-468 cells with CDC20 knockdown (shCDC20) or overexpression CDC20 (CDC20-OE) were pre-treated with 100 nM of docetaxel for 20 h. Pre-treated cells were cultured with either 50 nM of hesperadin or DMSO for 3, 6, 12, and 24 h in the presence of docetaxel. Immunoblot analysis was performed using antibodies against CDC20, pH3, MPM-2, Cyclin B1, PARP, and actin. The levels of pH3, cyclin B1, and MPM-2 were used as mitotic markers. (b) MDA-MB-468 cells were pre-treated with 100 nM of docetaxel for 20 h. Pre-treated cells were cultures with either 50 nM of hesperadin or DMSO for 3, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h in the presence of docetaxel. Cells were fixed with ice-cold ethanol, stained with propidium iodide staining solution, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are shown as the mean of two biological replicates. (c) Size of nuclei based on DAPI staining in MDA-MB-468 cells expressing CDC20 knockdown or overexpressing CDC20 (n = 50). (d) MDA-MB-468 cells expressing CDC20 knockdown or overexpressing CDC20 were transduced with mCherry-H2B. Cells were then analyzed by confocal microscopy to measure the percentage of condensed chromatin (n = 20). Data are shown as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001.