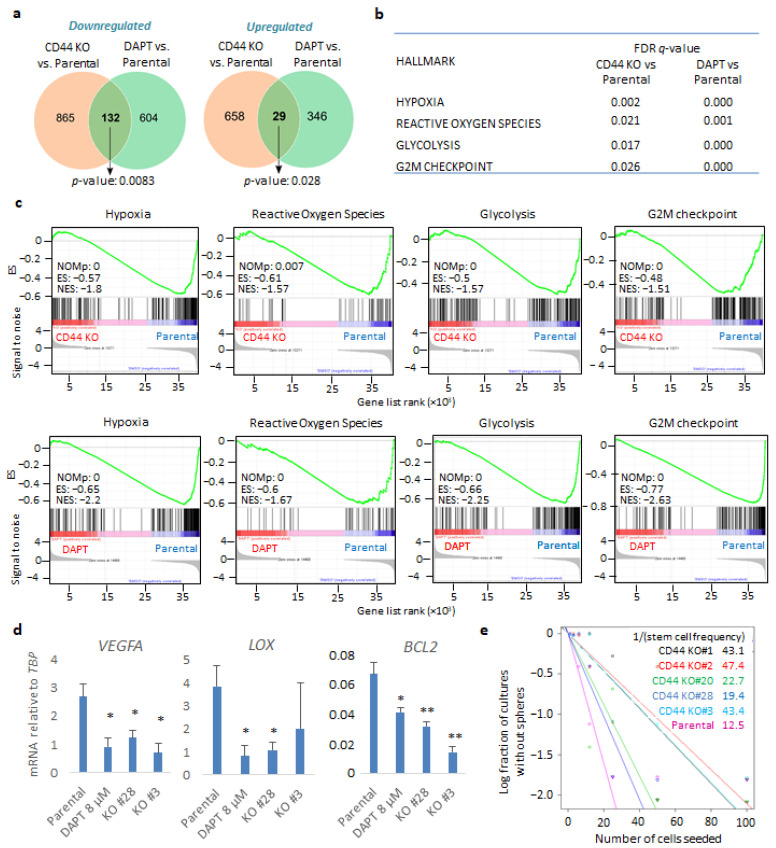
Figure 2.
CD44 genetic depletion and inhibition of CD44 cleavage leads to common gene signatures in U251MG cells grown in sphere-like conditions. (a) Venn diagram of overlapping down- or upregulated genes comparing parental U251MG cells to either CD44 KO cells or U251MG cells treated with the γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT; p-values are computed using Fisher’s Exact test. Cells were grown in low-attachment conditions. (b) FDR q-values of specific gene signatures (hallmarks) upon CD44 KO or treatment of parental U251MG with DAPT, compared to control cells. (c) Specific gene set enrichment analyses of the transcriptome between parental U251MG cells and CD44 KO cells, or parental U251MG cells treated with DAPT. ES, enrichment score; NES, normalized ES; NOMp, nominal p-value. (d) Hypoxia-related genes VEGFA, LOX, and BCL2 mRNAs were quantified in the respective conditions by RT-PCR and demonstrated after normalization to TBP. Asterisks show significant differences compared to the respective control condition: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (e) Extreme limiting dilution assay (ELDA) was carried out of either parental U251MG or CD44 KO clones; stemness capacity was evaluated after cells had been grown under non-adherent conditions for ten days. Steeper slopes indicate higher stem cell frequency. A table demonstrating average stem cell frequency per group is shown. All graphs show the average ± SEM values from at least three independent experiments.