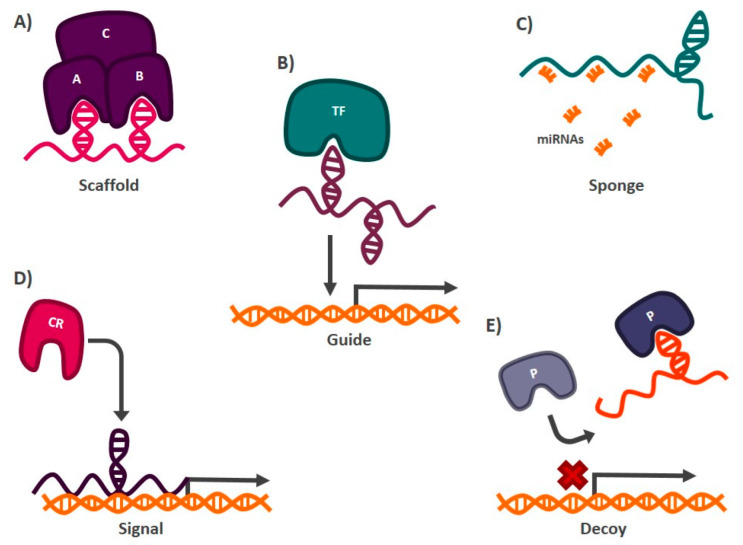
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of action of lncRNAs. (A) Scaffolds. They allow the formation of protein complexes. (B) Guides. They direct gene expression regulatory proteins or transcription factors (TFs) to sites in the genome where activation or inactivation of gene expression is demanded. (C) Sponges. They inhibit the activity of miRNAs by interacting directly with them. (D) Signals. They indicate to chromatin remodeling (CR) proteins the region of the genome where gene activation or silencing is required. (E). Decoy. They prevent the interaction of proteins (P) with their target by interacting directly with them.