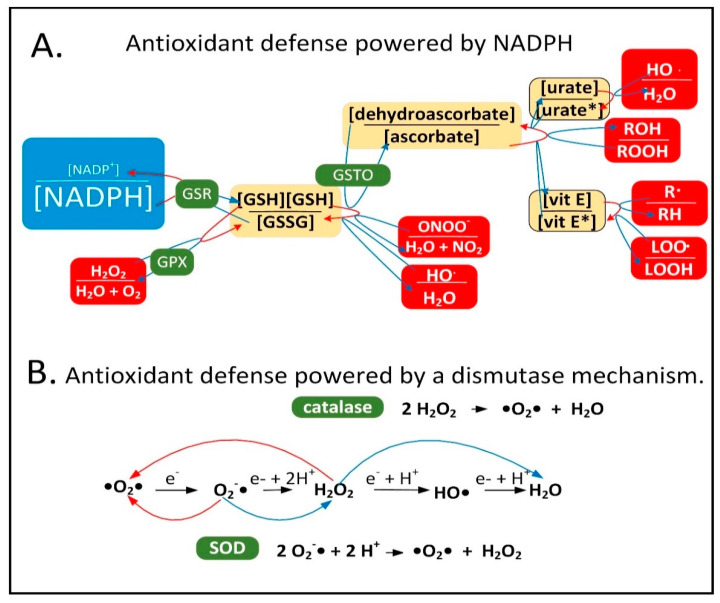
Figure 1.
Cellular antioxidants that use NADPH for reduction compared to those that use a dismutase mechanism. (A) NADPH provides electrons to the antioxidant system to detoxify ROS/RNS. Abbreviations: oxidized glutathione disulfide (GSSG), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), dehydroascorbate (oxidized form of vitamin C), peroxynitrite (ONOO−), hydroxyl radical (HO•), oxidized urate radical (urate*), oxidized vitamin E radical (vit E*), alkyl peroxide (ROOH), alkyl free radical (R•), lipid peroxide radical (LOO•) glutathione reductase (GSR), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), dehydroascorbate reductase (GSTO). (B) The dismutase mechanism of SOD and catalase uses two reactants (either two O2•− or two H2O2 molecules) and leads to the reduction of one and the oxidation of the other. Abbreviation: superoxide dismutase (SOD).