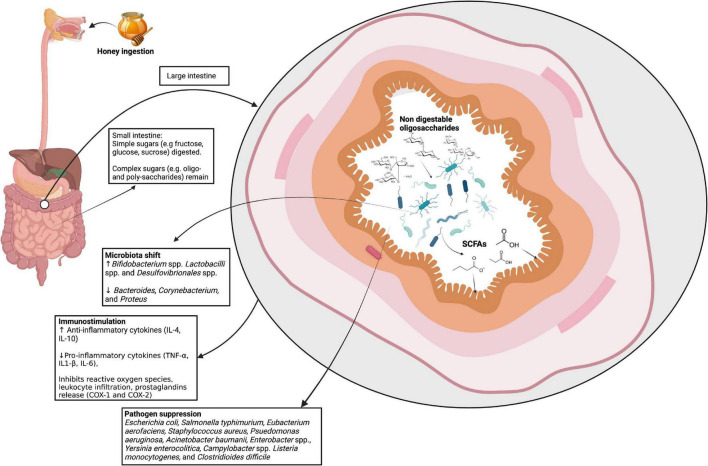
FIGURE 1.
The proposed prebiotic effects of honey. Following ingestion, the simple sugars in honey are absorbed in the small intestine. The non-digestible components, including oligosaccharides, reach the lower intestines where they are proposed to be involved in immunostimulation, modulating the microbiota, and suppressing pathogens. SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; COX, cyclooxegenase. Image created with BioRender.com.