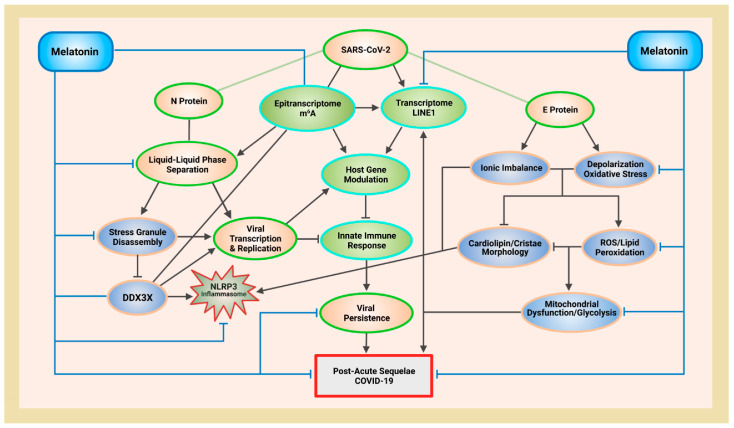
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrating melatonin attenuation of acute infection, viral persistence, and post-acute sequelae COVID-19 (PASC) from potential alterations to the epitranscriptome and transcriptome via RNA m6A modifications and LINE1 derepression by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The envelope (E) protein causes extensive mitochondrial distress and elevates oxidative stress via membrane depolarization and ionic imbalances that activate LINE1 derepression, NLRP3 inflammasome apoptotic signaling, stress granule formation, and nucleocapsid (N) protein liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). N protein LLPS forms membraneless condensates that not only facilitate viral transcription, genome packaging, and dissemination, but also enhance the suppression of host gene expression to evade innate immune responses via the disassembly of stress granules and the hijacking of DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX3X. Melatonin employs antioxidant-dependent and -independent strategies to modulate m6A modifications, suppress LINE1 derepression, rescue mitochondrial dysfunctions, and reduce oxidative stress. Melatonin regulates N protein LLPS to block the sequestration of DDX3X and the formation of NLRP3 inflammasome, as well as the disassembly of stress granules to support innate antiviral immune response, inhibiting viral transcription and replication, maintaining host gene stability and integrity to prevent severe disease and PASC (see Abbreviations for additional acronyms).