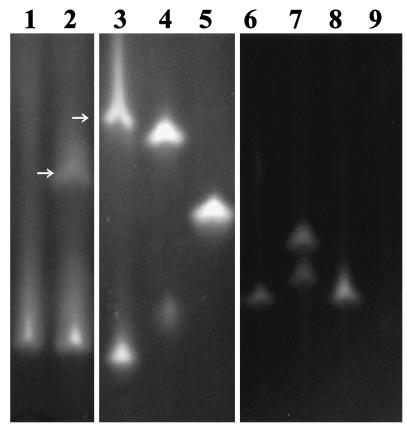
FIG. 6.
Native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel showing dehalogenases in crude cell extracts from the following αHA-utilizing bacteria: lane 1, E. coli(pYW10); lane 2, P. putida PP3; lane 3, P. putida AJ1; lane 4, Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3; lane 5, B. cepacia MBA4; lane 6, Burkholderia sp. strain K13; lane 7, Burkholderia sp. strain G02; lane 8, Burkholderia sp. strain I11; lane 9, Burkholderia sp. strain P11 (no αHA dehalogenase activity detected). Enzymes were visualized by activity straining with dichloroacetic acid (lanes 1, 2, and 6 to 9) or MCA (lanes 3 to 5) according to the method of Thomas et al. (59). Unless otherwise indicated, staining bands represent group II dehalogenases identified in separate zymography experiments by their activity with l-2MCPA but not d-2MCPA. Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 and Burkholderia sp. strain G02 each produced two separate group II dehalogenases. P. putida PP3 and AJ1 produced both group I (arrows) and group II dehalogenases.