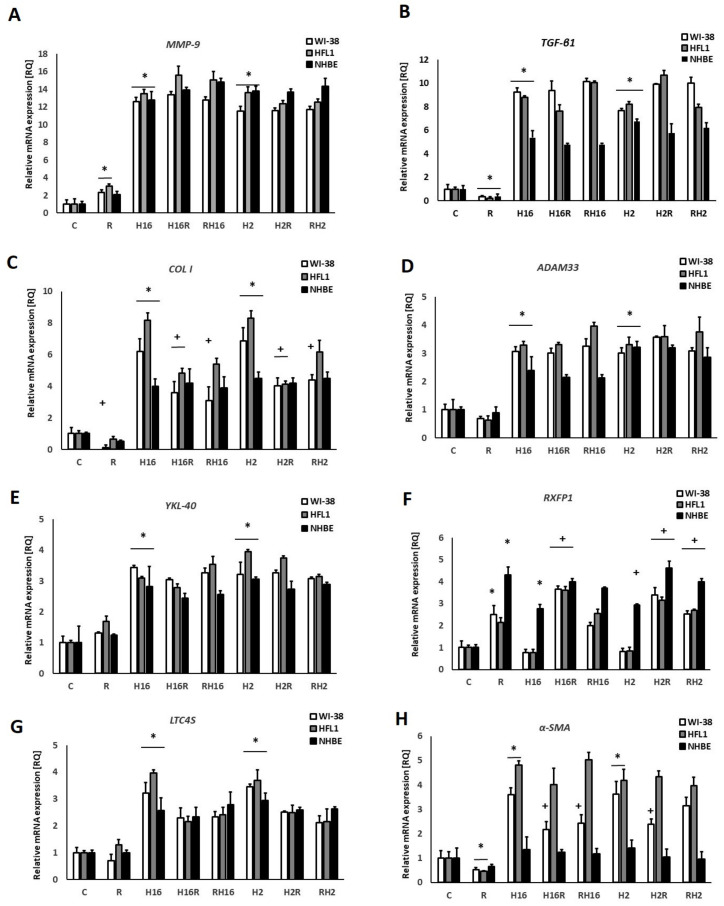
Figure 1.
qPCR analysis showing the effect of relaxin (R) on airway remodeling-involved genes. Human Rhinovirus (HRV-2 or HRV-16) induced the expression of all genes analyzed, except for the RXFP1 (Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1) gene. Relaxin induced mRNA expression of MMP-9 (matrix metalloproteinase-9, (A)), but reduced the expression of TGF-β (Transforming growth factor, (B)) and collagen I (C). It also induced mRNA expression of RXFP1 (Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1, (F)); no effect of relaxin was observed in ADAM33 (ADAM Metallopeptidase Domain 33), YKL-40 (Chitinase-3-like protein 1), and LTC4S (leukotriene C4 synthase) mRNA expression (D,E,G). Finally, relaxin inhibited HRV-induced expressions of collagen I (C) and α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin, (H). There were also no differences between the specimens when relaxin was added to HRV-infected cells or prior to the HRV infection: H16R, H2R—rhinovirus 16 and 2 added first, followed by relaxin—after 24 h, as well as RH16, RH2—relaxin added first, followed by rhinovirus-16 and 2—added after 24 h. * p < 0.05, in comparison to the control sample, and + p < 0.05 in comparison to the rhinovirus sample (HRV-2 or HRV-16, respectively); C is the control sample with medium only. N = 6, error bars—SEM.