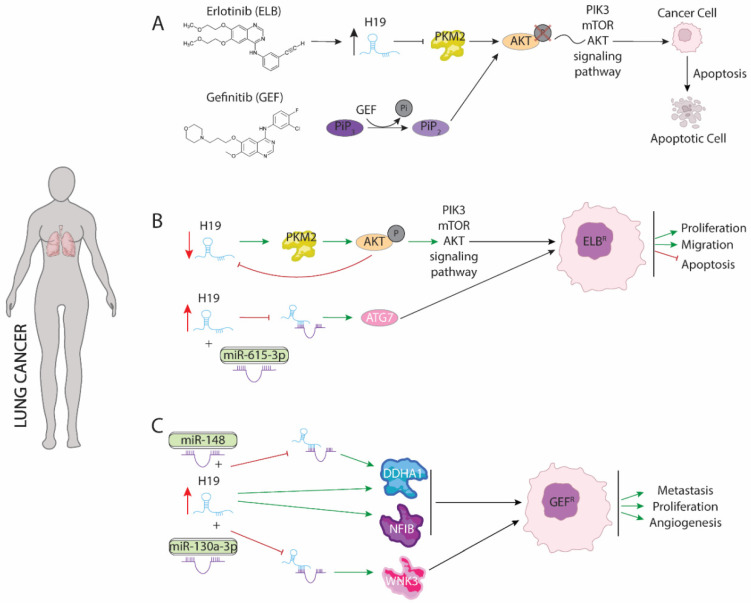
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of molecular mechanism dependent of H19 function in lung cancer. (A) Modes of action of Erlotinib (ELB) and Gefinitib (GEF) drugs involved in lung cancer treatment. (B) Dual role of H19 in acquired resistance to Erlotinib modulating PKM2 and ATG7 proteins. (C) Role of H19 as a sponge to binding miR-148 and miR-130a enhancing expression of DDHA1, NFIB and WNK3 proteins increasing proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis procedures.