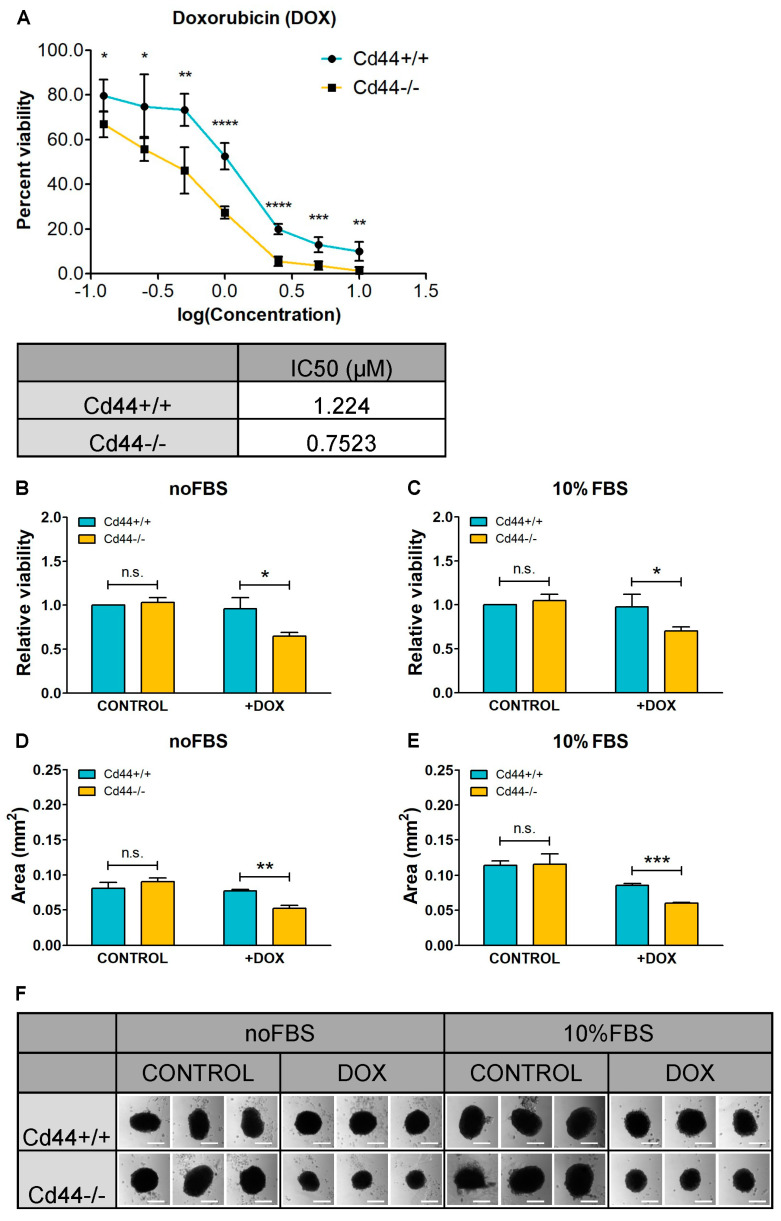
Figure 1.
Knockout of Cd44 sensitizes osteosarcoma cells to doxorubicin (DOX) treatment. (A) Determination of the half-maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration (IC50) of DOX. Dose-response curve of Cd44-positive and Cd44-negative osteosarcoma cells to DOX (upper panel) and corresponding IC50 values (lower panel) are shown. Cell viability was measured in quintuplicates in five independent experiments using WST1 assay. IC50 was calculated using GraphPad Prism and nonlinear regression. (B,F) Influence of DOX on formation of Cd44-positive and Cd44-negative spherical colonies. The histograms represent relative mean values of cell viability (B,C) or surface area (D,E) ±SD from three independent colony formation assays. Representative pictures of colonies formed in the presence or absence of DOX, either upon serum starvation or in medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) are shown in (F). Scale bar 200 µm. Student’s t-test values: n.s.: p > 0.05, *: p ≤ 0.05, **: p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001, ****: p ≤ 0.0001.