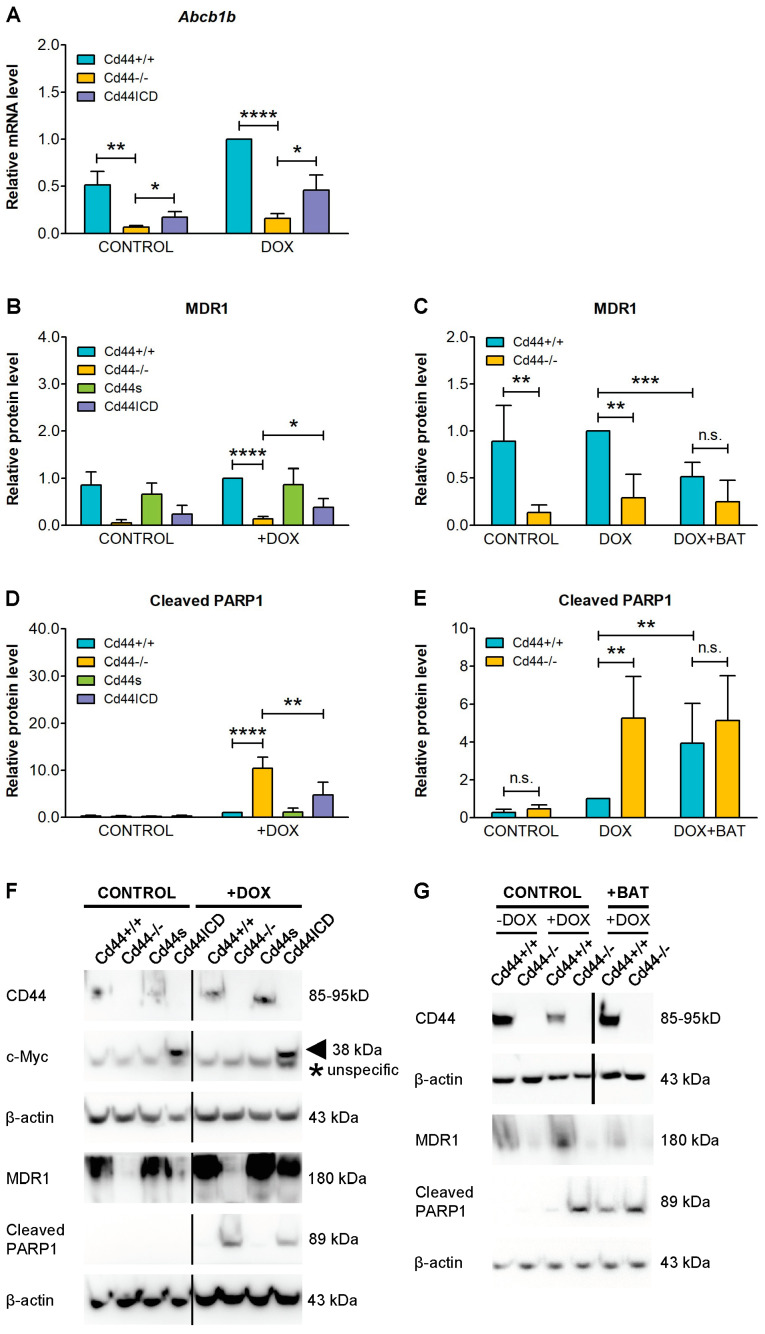
Figure 4.
Involvement of CD44 proteolytic cleavage in the regulation of MDR1 expression and doxorubicin (DOX) chemoresistance. (A) CD44 potentiates Abcb1b gene transcription. (B–G) Soluble intracellular domain of CD44 (Cd44ICD), mimicking cleavage product, significantly increases resistance to DOX; whereas, treatment with matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BAT) sensitizes Cd44-positive osteosarcoma cells to DOX. Cd44-positive wild-type cells, Cd44-negative cells, and cells with reconstituted expression of Cd44s and Cd44ICD were seeded at 60% confluency in DMEM medium supplemented with 7% FBS. The cells were incubated for 24 h with pure solvents (controls), 1.5 µM DOX or 10 µM batimastat and then harvested for immunoblot or RNA isolation. The histograms in (A–E) show mean values of mRNA or protein levels ± SD from three (A), four (B,C,E) or five (D) independent experiments. The values were normalized to loading control. Student’s t-test values: n.s.: p > 0.05, *: p ≤ 0.05, **: p ≤ 0.01, ***: p ≤ 0.001, ****: p ≤ 0.0001. Representative immunoblots are shown in (F,G). Arrowhead in (F) indicates CD44ICD, asterisk indicates unspecific band.