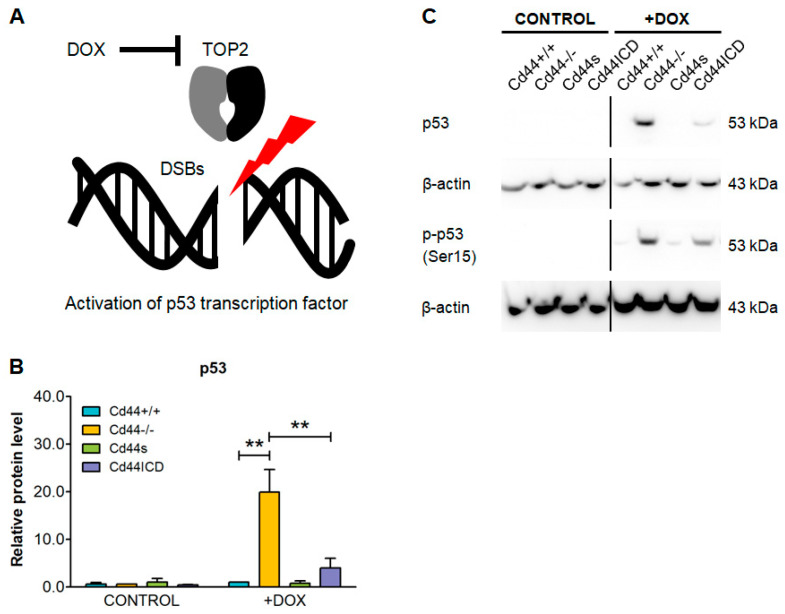
Figure 7.
Testing the effect of doxorubicin (DOX) on p53 level in osteosarcoma cells. (A) DOX inhibits topoisomerase II (TOP2) leading to DNA damage in the form of double-strand breaks (DSBs). As a consequence, the DNA damage response and p53 pathways are activated, which leads to cell cycle arrest and cell death. (B,C) DOX increases levels of active p53 in Cd44-negative osteosarcoma cells. The cells were treated as in Figure 4. The histogram in (B) shows mean value of p53 protein level ±SD from three independent experiments. The values were normalized to loading control. Student’s t-test values: **: p ≤ 0.01. Representative immunoblots for detection of total and phosphorylated p53 are shown in (C). Please notice that phosphorylated p53 was detected by reprobing lower membrane part from the experiment in Figure 4F, therefore the β-actin is the same.