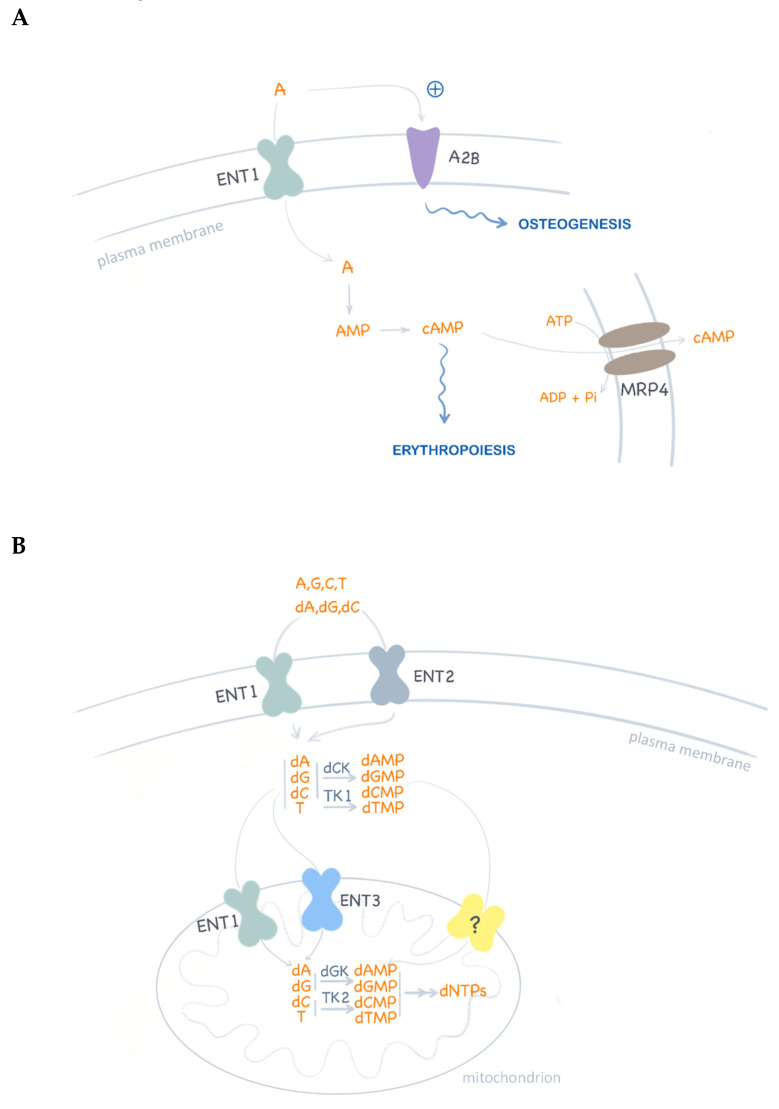
Figure 3.
ENT1 functions in nucleotide metabolism. (A) Schematic representation of adenosine (A) translocation and signaling. Adenosine activation of P1 receptors (i.e., A2B) promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Intracellular cAMP levels are modulated by ENT1-associated adenosine translocation and also by MRP4 cAMP efflux. In turn, cAMP homeostasis is critical for erythropoiesis regulation. (B) Nucleoside uptake at the plasma membrane is mediated by ENT1 and ENT2 homo and hetero-oligomeric complexes. ENT1 has been reported to translocate nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in mitochondria. In ENT1 null cells, deoxynucleoside supply to mitochondria may be maintained by ENT3 function, although the proven functional expression of an unknown deoxynucleotide transporter (?) may be the best compensatory mechanism to maintain mitochondrial deoxynucleotide pools for DNA replication.