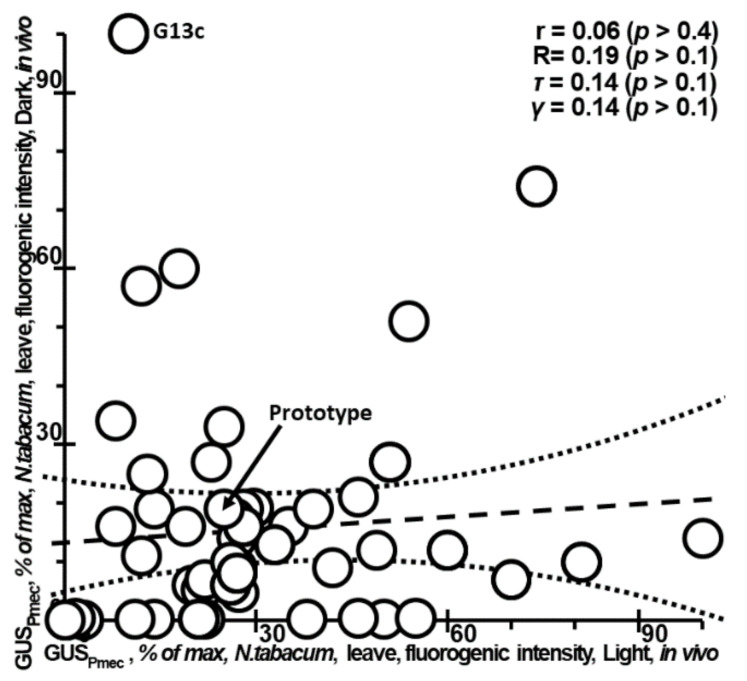
Figure 1.
The effects of mutation within the analyzed artificial Pmec promoter on the β-glucuronidase (GUS) activity of tobacco under the experimental conditions “light” (x-axis) and “dark” (y-axis) in vivo [53] do not correlate with each other, thereby casting doubt on both the existence and the uniqueness of the uniform estimate for the mutational effects of plant proximal promoters on gene expression under various environmental conditions, usually called an ill-posed inverse problem [61]. Legend: circle, the prototype (arrow, →), or a mutant variant of the studied artificial promoter Pmec for plants; dashed and dotted lines are linear regression and limits of its 95% confidence interval, as calculated in the Statistica software (StatsoftTM, Tulsa, OK, USA); r, R, τ, γ, and p are the linear correlation, Spearman’s rank correlation, Kendall’s rank correlation, Goodman–Kruskal generalized correlation coefficients, and their statistical significance, respectively.