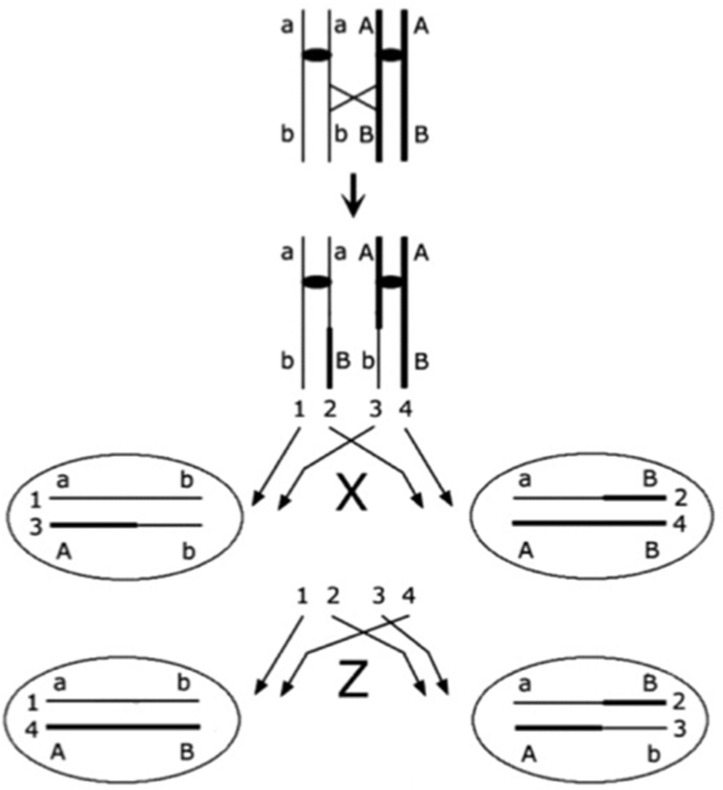
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of mitosis with crossing over. Each segment represents a chromatid, with sister chromatids linked by a centromere (black oval); crossing over (diagonal cross) occurs between the centromere and locus B. Two types of segregation are possible (Stern [51]): z segregation, in which the two recombinant chromatids (2 and 3) segregate together, apart from the two non-recombinant chromatids (1 and 4); and x segregation, in which each recombinant chromatid segregates with the non-sister non-recombinant chromatid. Loss of heterozygosity occurs for all loci distal to the site of crossing over with x segregation (in this example, at locus B).