Figure 1:
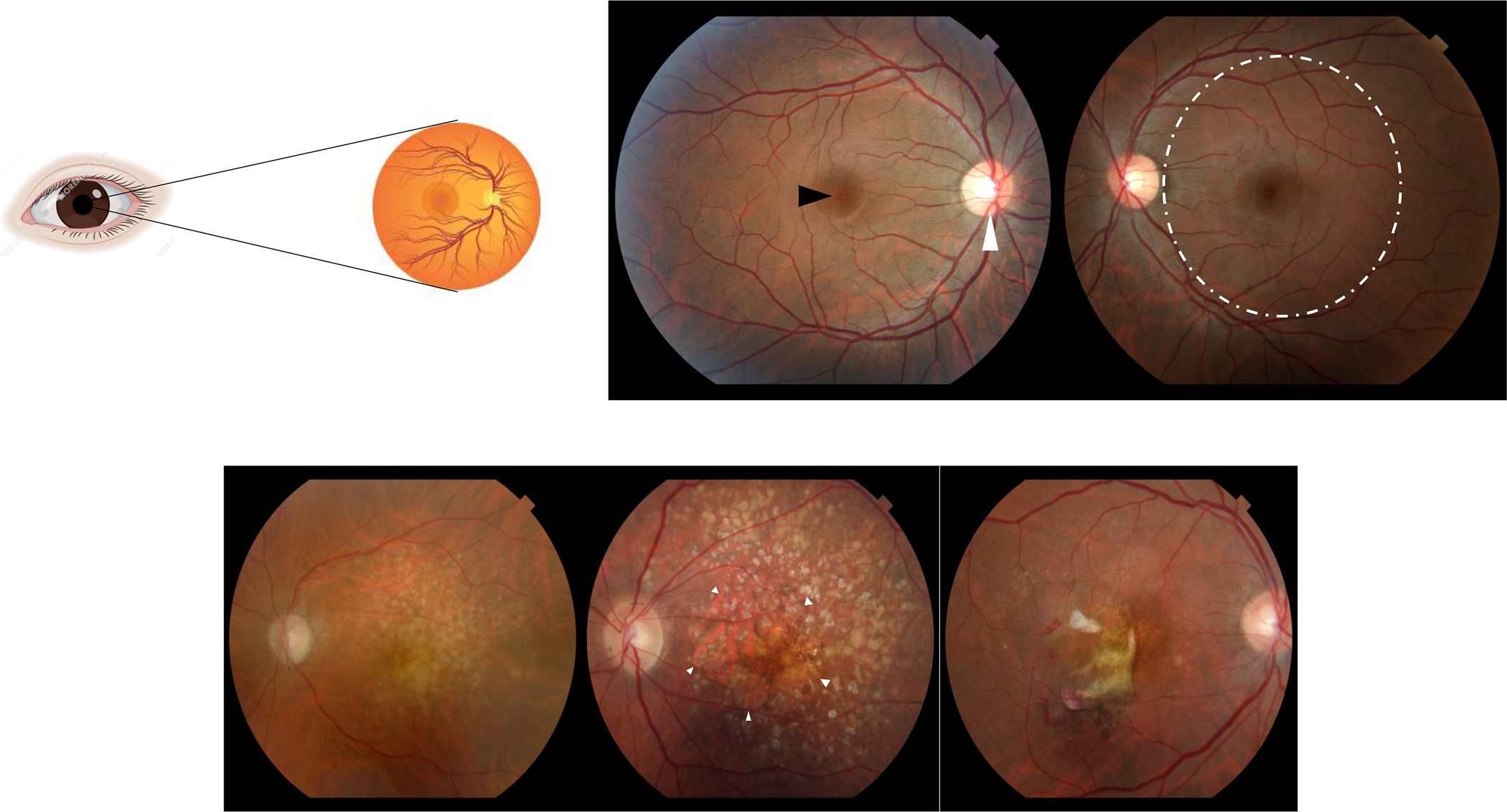
A sagittal section of the normal human eye is represented on the top left. Light photons enter the eye and visual transduction begins in the neurosensory retina (top left). Slit lamp biomicroscopic examination allows examination of the patient retinas (top right panel; central part of the retina called macula = dashed circle, center of the macula called fovea = black arrowhead, optic nerve head = white arrowhead). Fundus photographs illustrate features of AMD visualized by slit lamp biomicroscopy (bottom panel): (left) Intermediate AMD identified by yellowish deposits underneath the retina called drusen, (middle) advanced non-neovascular AMD characterized by geographic atrophy (arrowheads) in the setting of drusen, and (right) neovascular AMD diagnosed by hemorrhage and fluid associated with choroidal neovascularization
