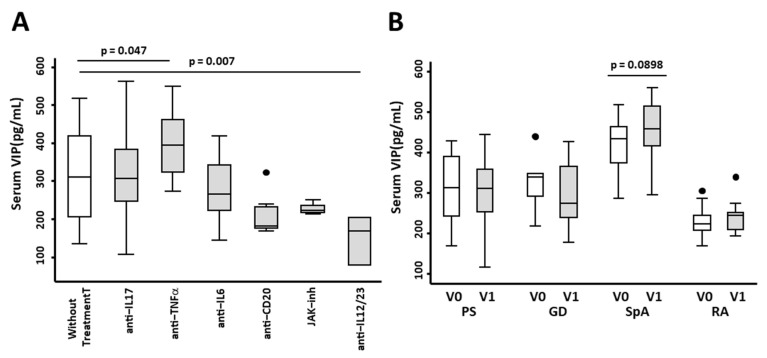
Figure 3.
Effect of biological therapies on the expression of serum VIP levels in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). (A) Serum VIP levels (pg/mL) of 38 healthy donors without treatment and 9 IMID patients with anti-IL17 treatment, 15 with anti-TNFα treatment, 10 with anti-IL6 treatment, 8 with anti-CD20 treatment, 4 with JAK inhibitors, and 2 with anti-IL12/23 treatment are shown. Statistical significance was calculated using the variable of serum VIP levels normalized by inverse square root and applying ANOVA and Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons to obtain the p-values as indicated. In all panels, data are presented as the interquartile range (p75: upper edge of the box, p25: bottom edge of the box, and p50: midline) and p90 and p10 (lines below and above the box) of the serum VIP levels. Dots represent outliers. Significance threshold was set at p < 0.05. (B) Serum VIP levels (pg/mL) by ELISA of 15 patients with psoriasis (PS), 8 with Graves’ disease (GD), 15 with spondyloarthritis (SpA), and 14 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) before (V0) and after 2–4 months (V1) of treatment with biological therapies are shown. To analyze the differences in serum VIP levels before and after treatment, paired sign test was used. Significant differences between groups are shown in the figure.