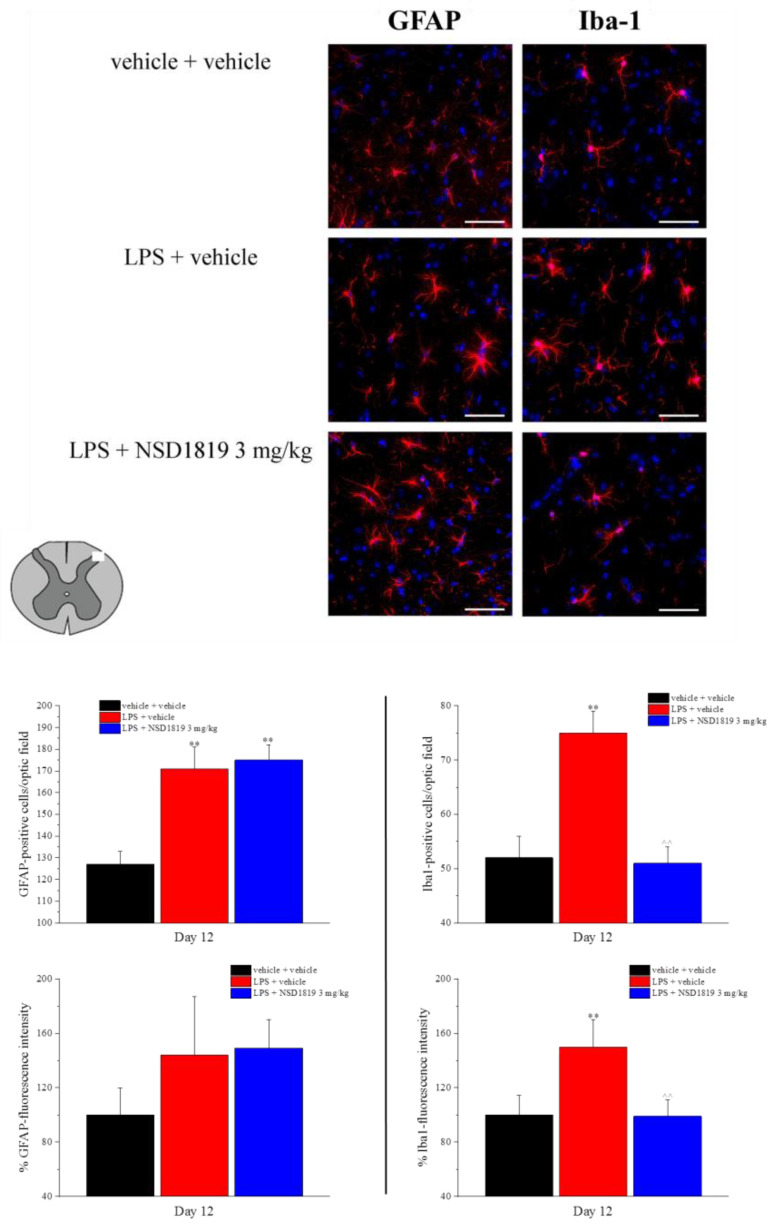
Figure 6.
Effect of NSD1819 on LPS-induced glia cell activation in the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord (L4–L5). LPS (1 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected for five consecutive days (from 1 to 5). NSD1819 was suspended in 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt (CMC) and daily orally administered, starting from day 1 until the end of the experiment. Control animals were treated with vehicles. At the end of the behavioral experiments and 16 h after the last administration of the compound, animals were sacrificed, and the lumbar spinal cord was collected. GFAP and Iba-1 antibodies were used as marker for astrocytes and microglia, respectively. Representative images of merged GFAP-or Iba-1-labeled cells (red), plus DAPI-labeled cell nuclei (blue) at 40× magnification are shown (scale bar = 50 μm). Histograms show the quantitative analysis of GFAP and Iba-1 fluorescence intensity and the number of GFAP- and Iba-1 positive cells/optic field. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. of values from 8 mice analyzed in 2 different experimental sets. ** p < 0.01 vs. vehicle + vehicle; ^^ p < 0.01 vs. LPS + vehicle.