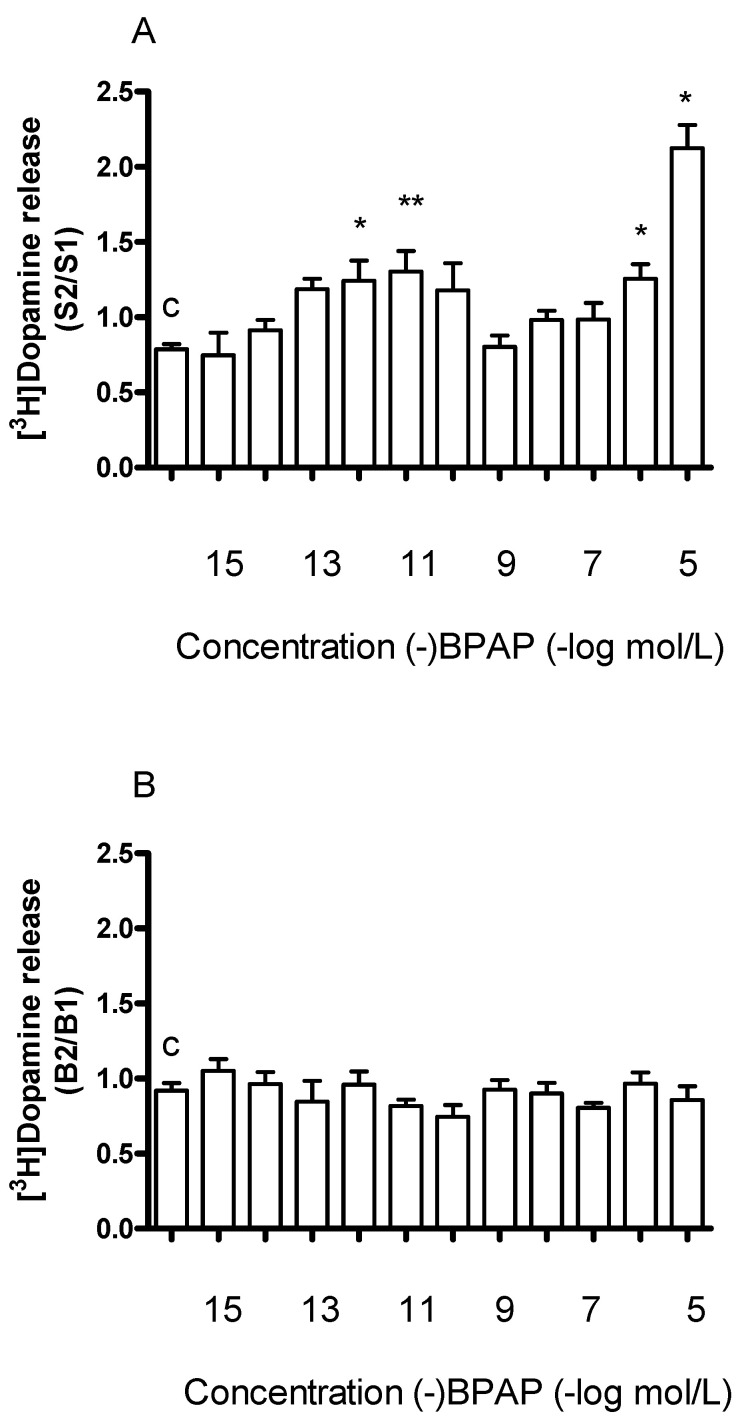
Figure 6.
Concentration-dependent effect of (−)BPAP on resting and electrical stimulation-induced [3H]dopamine release from rat striatum. For the experimental procedure, see Figure 2A. (−)BPAP was added in a concentration range from 10−15 to 10−5 mol/L to the superfusion buffer from fraction 8 and maintained through the experiment. (A) The S2/S1 ratio indicates the effect of (−)BPAP on electrical stimulation-induced [3H]dopamine release determined in 1st (absence of drug, S1) and 2nd (presence of drug, S2), stimulations were carried out in fractions 4 and 18. The S2/S1 value was 0.79 ± 0.04 in control experiments (c). One-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett’s test, F(11,48) = 10.16, p < 0.0001, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, mean ± S.E.M., n = 4-8. (B) The B2/B1 ratio indicates the effect of (−)BPAP on resting fractional [3H]dopamine release determined in fractions 3 (absence of drug, B1) and 17 (presence of the drug, B2). The B2/B1 value was 0.91 ± 0.05 in control experiments (c). One-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett’s test, F(11,48) = 1.171, p = 0.331, mean ± S.E.M., n = 4-8.