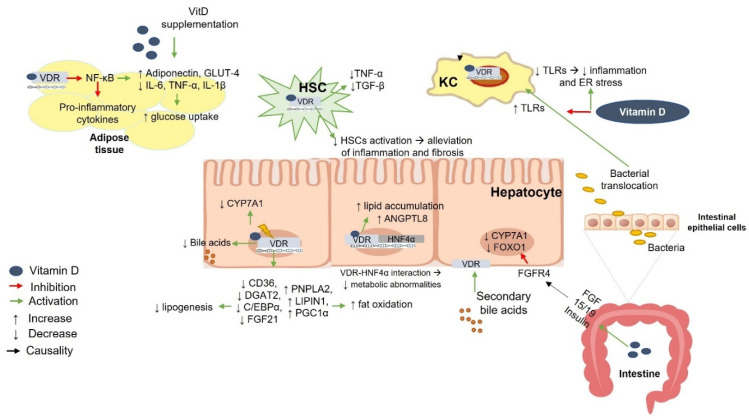
Figure 5.
Vitamin D–VDR-mediated effects on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Vitamin D acts on adipose tissue by inhibiting NF-κB transcription and suppressing the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Higher adiponectin secretion improves insulin resistance by promoting transcriptional regulation and translocation of GLUT4 into adipocytes, leading to improved glucose uptake. Increased gut permeability leads to translocation of bacteria, which in turn induce TLRs on KCs. Vitamin D suppresses the expression of TLRs in KCs and reduces inflammation. Binding of vitamin D to VDR leads to reduced proliferation of HSCs, thereby contributing to the alleviation of liver fibrosis. Co-localization of VDR with HNF4α in the nucleus ameliorates metabolic abnormalities. Vitamin D upregulates intestinal FGF15 (human ortholog FGF19), which phosphorylates hepatic FGFR4 in the liver to inhibit CYP7A1. Insulin and FGF15/19 suppress FOXO1, a key mediator of the FGF and insulin pathways, contributing to bile acid and glucose metabolism. Stimulation of VDR accelerates lipid accumulation in the liver and increases the expression of ANGPTL8, a key modulator of triglyceride metabolism. The deletion of VDR and apolipoprotein E results in decreased gene expression of CD36, DGAT2, C/EBPα, and FGF21 and increased expression of PNPLA2, LIPIN1, and PGC1α in mouse livers. VDR, vitamin D receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4; FGF15/19, fibroblast growth factor 15/human ortholog 19; FGFR4, FGF receptor 4; FOXO1, forkhead transcription factor 1; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7a-hydroxylase; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 α; ANGPTL8, angiopoietin like 8; CYP27B1, cytochrome P450, family 27, subfamily B, polypeptide 1; HSC, hepatic stellate cells; KC, Kupfer cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IL-, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36); DGAT2, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2; C/EBPα, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; PNPLA2, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 2; PGC1α, peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha.