Figure 1.
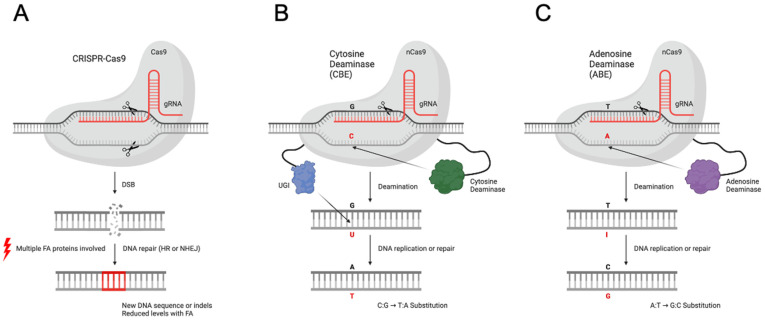
Bypassing DSB induction with base editor technology is ideal for FA gene therapy. (A) CRISPR-Cas9 produces DSBs that are difficult for FA-mutated cells to resolve during gene therapy; a designed sgRNA complex with Cas9 nuclease which localizes and binds to the complementary target site. Cas9 creates a DSB in the DNA that the cell resolves through the error prone NHEJ pathway or the HDR pathway, although to reduced levels in FA-mutated cells. (B) CBE; nCas9, which instead only nicks the opposite target stand, induces a DNA repair pathway response. The target C in the editing window is deaminated by a fused APOBEC1 protein to a U, and a fused uracil glycosylase inhibitor (UGI) protein prevents the cell from resolving this mismatch through the BER pathway. During DNA replication or repair, the U matches with an A resulting in a C/G to T/A substitution. (C) ABE; nCas9, which also only nicks the opposite target stand, induces a DNA repair pathway response. The target A in the editing window is deaminated by a fused TadA protein to an inosine, I. During DNA replication or repair, the I is read as a G resulting in an A/T to G/C substitution.