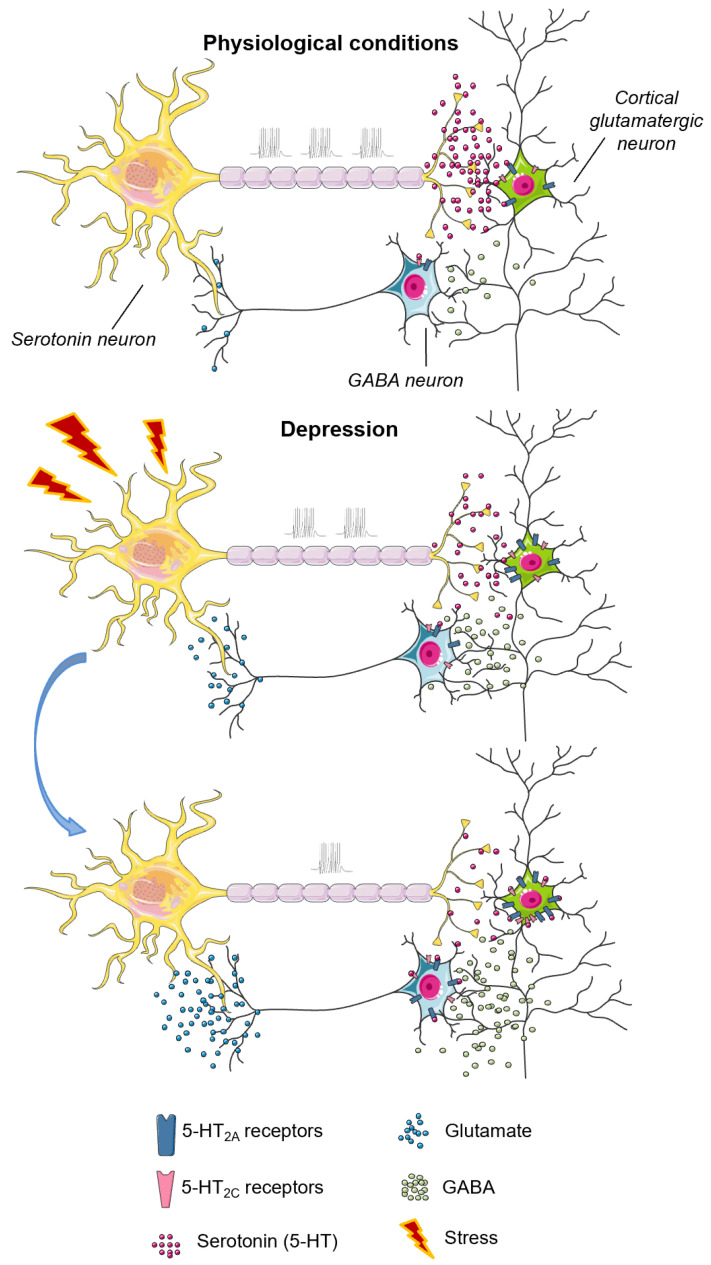
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of mechanisms of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor involvement in the pathogenesis of depression. Under physiological conditions, postsynaptic 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors regulate glutamate and/or GABA release; upon stress-induced serotonin depletion, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors are upregulated and sensitized. Sensitized 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors indirectly inhibit serotonergic neurotransmission, aggravate serotonin deficit and provoke depressive-like behavior.