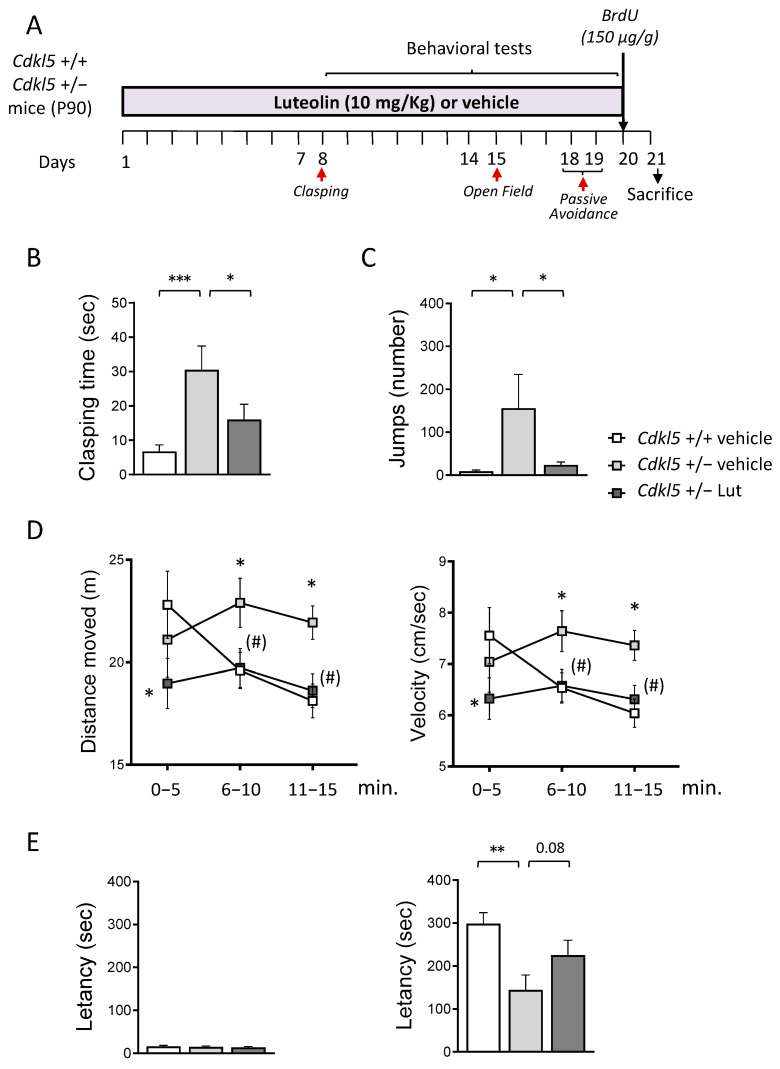
Figure 1.
Effect of luteolin treatment on behavior of Cdkl5 +/− mice. (A) Experimental plan. Starting from postnatal day 90 (P90), Cdkl5 +/− female mice were treated with vehicle or luteolin (i.p. 10 mg/kg) for 20 days. Behavioral tests were performed during the last two weeks of treatment. Red arrows indicate the day on which the behavioral tests were performed. The day before sacrificed mice received a single subcutaneous injection of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU 150 µg/g). (B) Total amount of time spent hind-limb clasping during a 2-min interval in vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ (n = 21) and Cdkl5 +/− (n = 18) mice and luteolin-treated Cdkl5 +/− (n = 18) mice. (C) Number of stereotypic jumps (repetitive beam breaks < 1 s) in the corners of the open field arena during the 15-min trial in vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ (n = 19) and Cdkl5 +/− (n = 18) mice and luteolin-treated Cdkl5 +/− (n = 17) mice. (D) Locomotor activity measured as average locomotion velocity (right graph) and total distance travelled (left graph) during a 15-min open field test in vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ (n = 19) and Cdkl5 +/− (n = 18) mice and luteolin-treated Cdkl5 +/− (n = 17) mice. (E) Passive avoidance test on vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ (n = 21) and Cdkl5 +/− (n = 18) mice and luteolin treated Cdkl5 +/− (n = 17) mice. Graphs show the latency to enter the dark compartment on the 1st day (on the left) and on the 2nd day (on the right) of the behavioral procedure. Values represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 as compared to the vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ condition; (#) p < 0.065 as compared to the vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/− condition. Fisher’s LSD test after one-way ANOVA for data set in (B,C,E) and after two-way ANOVA for data set in (D).