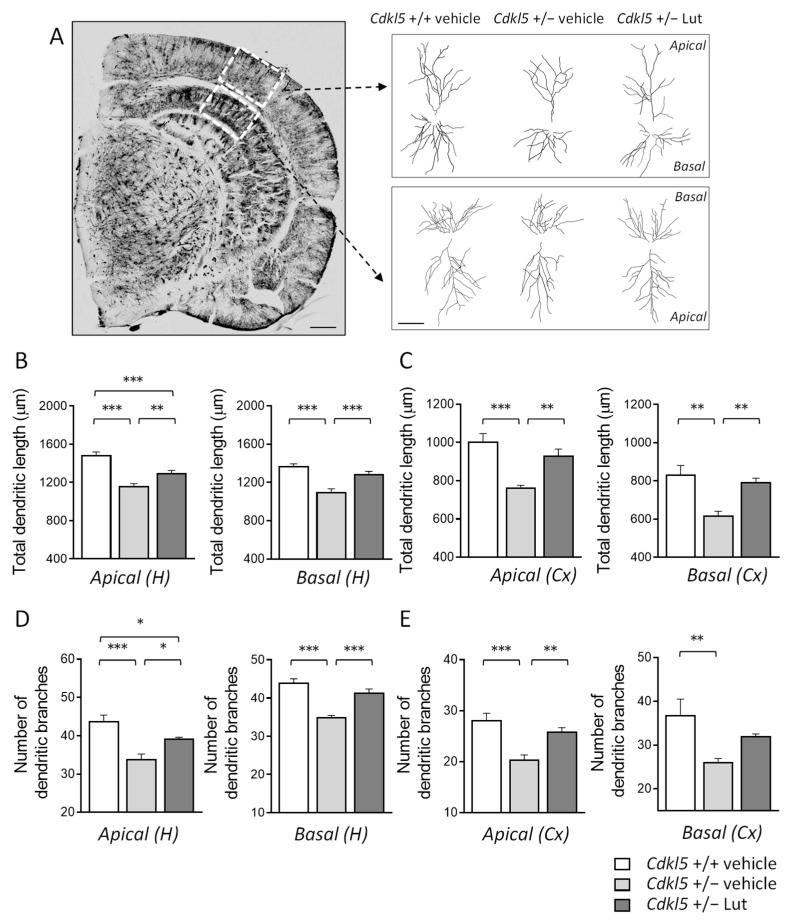
Figure 4.
Effect of luteolin treatment on dendritic architecture of hippocampal and cortical neurons of Cdkl5 +/− mice. (A) Representative image of a Golgi-stained section (panel on the left; scale bar = 500 μm), showing the portion of hippocampal and cortical regions where the dendritic arbor of pyramidal neurons was traced (areas enclosed in the dashed square). On the right, examples of the reconstructed apical and basal dendritic tree of Golgi-stained cortical (upper) and CA1 (lower) pyramidal neurons of one animal from each experimental group. Scale bar = 40 μm. (B,C) Total dendritic length of apical (on the left) and basal (on the right) dendrites of Golgi-stained pyramidal neurons in the CA1 field (B) and cortex (C) of vehicle-treated Cdkl5 +/+ (n = 4) and Cdkl5 +/− (n = 4) mice and luteolin-treated Cdkl5 +/− (n = 4) mice. (D,E) Number of dendritic branches of apical (on the left) and basal (on the right) dendrites of Golgi-stained pyramidal neurons in the CA1 field (D) and cortex (E) of mice as in (B). H = hippocampus; CX = cortex. Values are represented as means ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Fisher’s LSD test after one-way ANOVA.