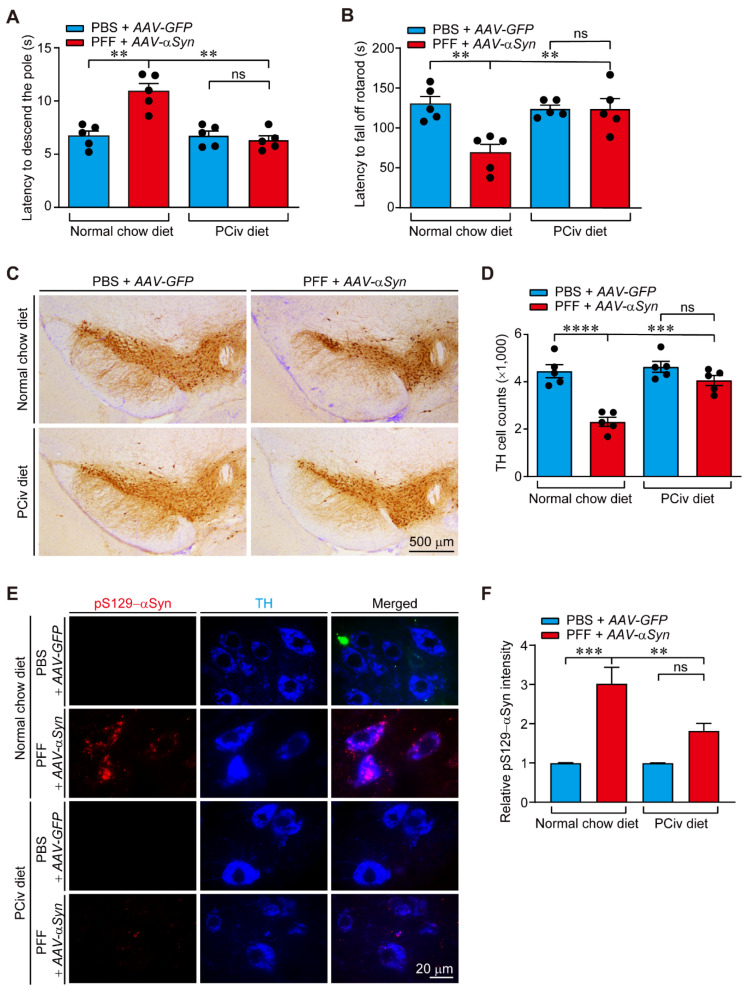
Figure 4.
PCiv administration suppresses PFF-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration, α-synuclein aggregation, and motor dysfunction in vivo. (A) Bradykinesia (slowness of movement) assessed by pole test for control and combinatorial PFF/AAV-αSyn-injected mice with or without PCiv treatment (50 mg PCiv/kg diet for 30 days, n = 5 per group). Control mice are those nigrally injected with PBS and AAV-GFP. (B) Motor coordination of the mice in the experimental group was assessed by an accelerated rotarod test (n = 5 per group). (C) Representative tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemical staining of the ventral midbrains of control and combinatorial α-synucleinopathy-PD mice fed with a PCiv diet (50 mg/kg diet for 30 days) or normal chow diet. (D) Stereological assessment of TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the injection side of the indicated mice groups (n = 5 mice per group). (E) Representative immunofluorescence images of pS129-αSyn and TH in the substantia nigra coronal sections of the indicated experimental mice groups. (F) Quantification of relative pS129-αSyn fluorescence intensities in the TH-positive dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra sections from the indicated experimental groups (n = 28 cells from 3 mice per group). The quantified data are expressed as means ± SEMs. Statistical significance was determined by an ANOVA test with Tukey’s post hoc analysis, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. ns = nonsignificant.