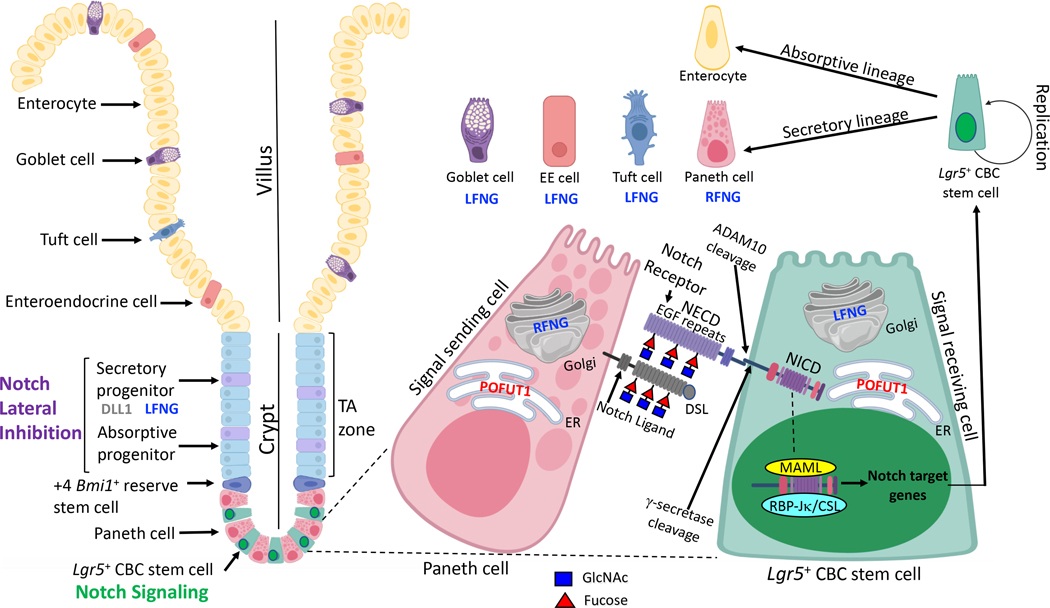
Figure 1. Notch signaling in intestinal epithelium.
Lgr5+ CBC stem cells expressing NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 are present at the bottom of crypts interspersed with Paneth cells. Paneth cells express Notch ligands DDL1, DLL4 and JAG1 which stimulate Notch signaling in CBC stem cells. O-glycans attached to EGF repeats on the ECD of Notch receptors regulate receptor and ligand binding. Notch ligands also have EGF repeats modified by O-glycans, and bind Notch receptors via their N-terminal Delta-Serrate-LAG-2 (DSL) domain. POFUT1 initiates formation of O-fucose glycans by adding O-fucose to the consensus site present in numerous EGF repeats of NECD. O-fucose is extended by the addition of GlcNAc by LFNG or RFNG. LFNG is expressed in CBC stem cells, at increased levels in progenitors of the TA zone, and by goblet cells, enteroendocrine (EE) and Tuft cells. RFNG is expressed by Paneth cells. Interactions between Notch receptor O-glycans and Notch ligands determine the strength of Notch signaling, which regulates the replication and differentiation of CBC stem cells. Secretory lineage progenitors expressing DLL1 and LFNG induce lateral inhibition of enterocyte progenitors in the TA zone to control the balance of cell fate decisions and differentiated cells of the villus. The figure was created in part with Biorender.com.