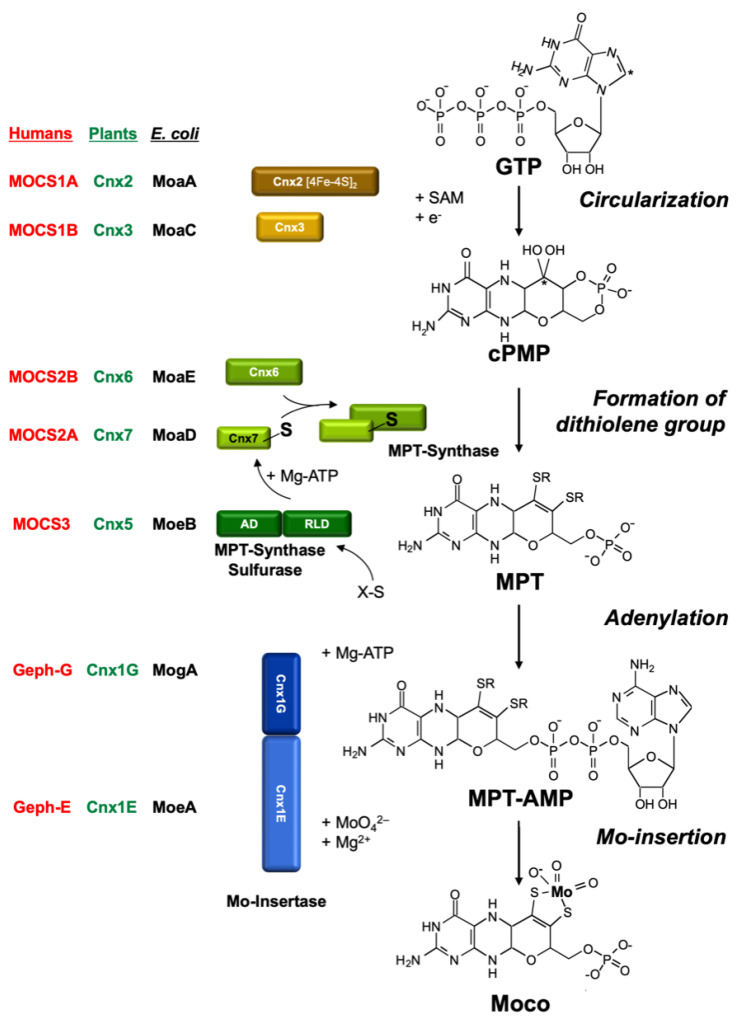
Figure 3.
Pathway of Moco biosynthesis in eukaryotes. The pathway can be divided into four steps, each being characterized by its main features as given in italics on the right side. The names for the proteins from the plant Arabidopsis thaliana (green), humans (red), and E. coli (black) catalyzing the respective steps are given. In GTP, the C8 atom of the purine is labeled with a star. This carbon is inserted between the 2′ and 3′ ribose carbon atoms, thus forming the new C1′ position in the four-carbon side chain of the pterin (labeled with a star in cPMP). The in vivo sulfur (X-S) source for Cnx5 and MOCS3 is probably cysteine. Steps three and four in eukaryotes are catalyzed by the individual domains of Cnx1 (G and E) or Gephyrin (G and E). Functional properties such as [Fe–S] clusters in Cnx2 and Mocs1A, the use of S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), adenylation, and sulfuration of the small subunit of MPT synthase (Cnx7 and Mocs2B, respectively) are indicated. In Cnx5, MoeBD denotes the MoeB-like domain and RLD the rhodanese-like domain. Modified after Mendel and Kruse [93].