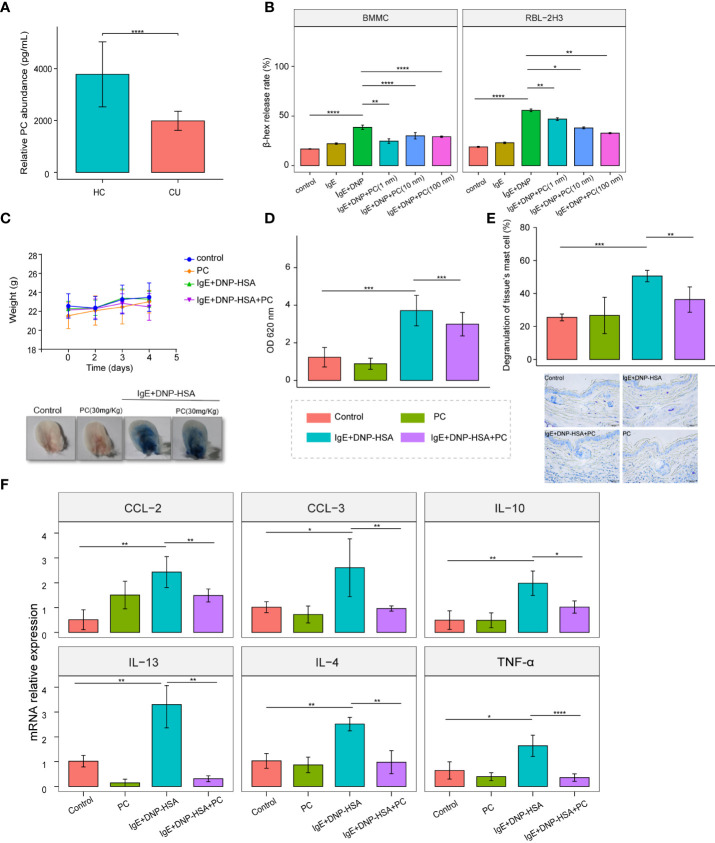
Figure 5.
Supplementation with PC attenuates IgE-induced mast cell activation in vitro and in vivo. (A) The mean plasma PC level of the CU patients n = 42 was significantly lower than that of the HC subjects n = 42 were determined by ELISA. (B) PC (Including three concentrations: 1 nM,10 nM, and 100nM) inhibited the degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells and BMMCs, and there was no concentration dependence. (C) Bodyweight curve and phenotypic changes of four mice groups (Control, n = 5; PC, n = 5; IgE+DNP-HSA, n = 8; IgE+DNP-HSA+PC, n = 8) during the experiment. (D) PC intervention reduced skin vascular permeability in the PCA mice model. (E) Toluidine blue staining showed that PC inhibited degranulation of skin mast cells. (F) The expression of genes involved in cytokine was measured by real- time-qPCR analysis. PC inhibited cytokine release in PCA mice models, including IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, CCL-2, CCL-3, and TNF- α. The data from multiple experiments were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Significant differences were evaluated using student t-test or the nonparametric test (Be denoted as follows: ****p≤.0001, ***p ≤.001, **p ≤.01, *p ≤.05).