Extended Data Fig. 7. Functional analysis of UvrDΔCTD and RNAPΔβi4.
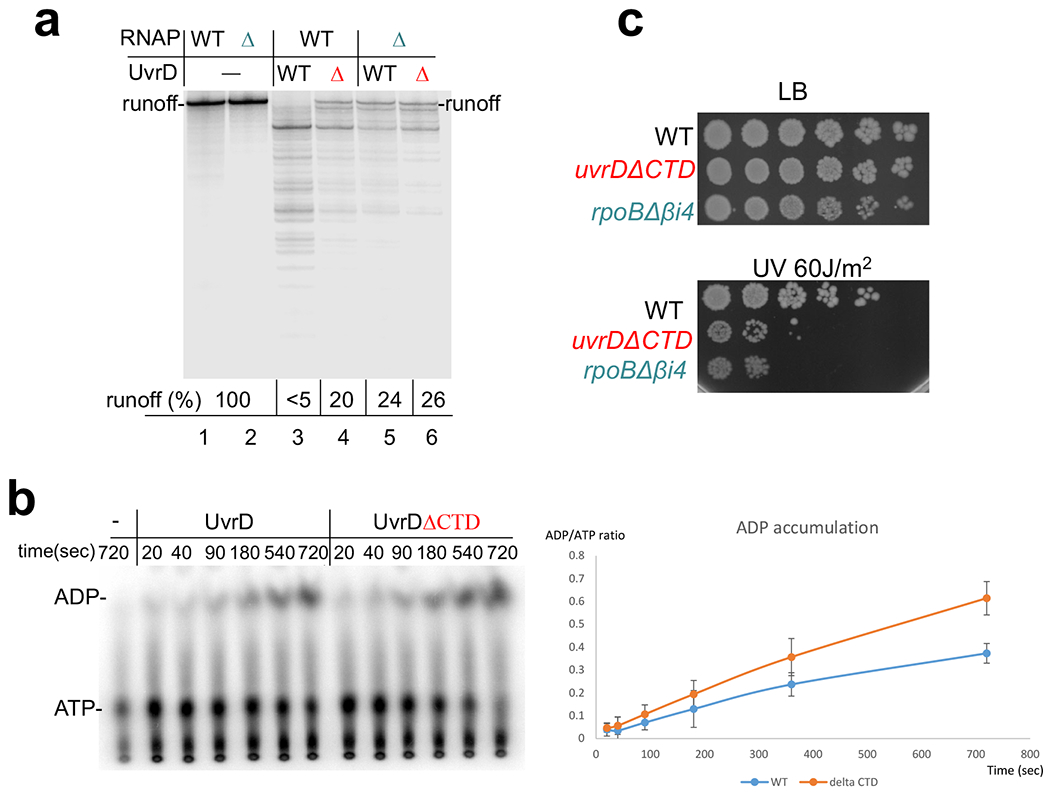
a, Deletions of the CTD of UvrD or βi4 of RNAP partially compromise UvrD-mediated backtracking. EC20 was formed by the wt RNAP or RNAP lacking βi4 (green Δ) (lanes 13 to 18) at the T7A1 DNA template and then chased in the presence of specified amounts of UvrD (red Δ). The pro-backtracking activity of UvrD was assessed as a ratio (%) between the amount of full length (runoff) product and total amounts of RNA products located below the runoff. Majority of these products are the result of UvrD-mediated backtracking and sensitive to transcript cleavage by GreB9,15. b, Deletion of the CTD does not compromise UvrD catalytic activity. The autoradiogram shows the thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate of UvrD-mediated ATP hydrolysis. The reaction was performed using polyC single stranded DNA template as described in Methods. The means ± SE from three experiments are plotted on the right. c, uvrDΔCTD and Δβi4 cells are equally more sensitive to genotoxic stress as compared to wt. Representative efficiencies of colony formation of wt (MG1655) and mutant cells following treatment with the indicated dose of UV irradiation. Cells were grown to OD600 ~0.4 and serial 10-fold dilutions were spotted on LB agar plates followed by UV irradiation and incubation in the dark at 37 °C for 24 h.
