Extended Data Fig. 9. Effects of high (750 μg/ml) and low (50 μg/ml) Rif on E. coli transcription and NER.
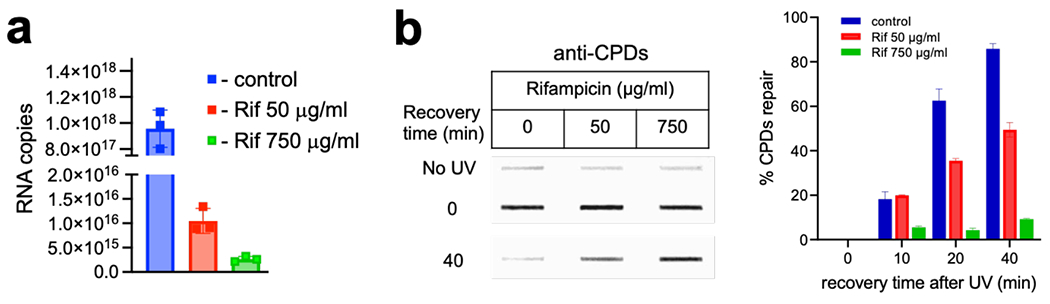
a, Inhibition of chromosomal lacZ transcription by Rif. Copies/μL cDNA of lacZ transcripts was determined using absolute quantification (see Methods). A standard curve was generated using lacZ PCR product (1016 to 1023). RT-qPCR was performed using cDNA isolated from bacterial cultures treated with indicated concentrations of Rif. Number of copies of lacZ transcripts was determined by interpolation. Values are the means ± SD (n = 3). b, Inhibition of CPDs repair by high and low Rif. (Left panel) Representative slot blot probed by fluorescently labeled secondary antibody to reveal binding of primary monoclonal CPD-specific antibodies (see Methods). (Right panel) Quantitative analysis of slot blot images for the indicated recovery time points post-UV. Bars, standard errors of the means from 3 independent experiments.
