Extended Data Fig. 19. An overview of the automated dimer-assembly workflow.
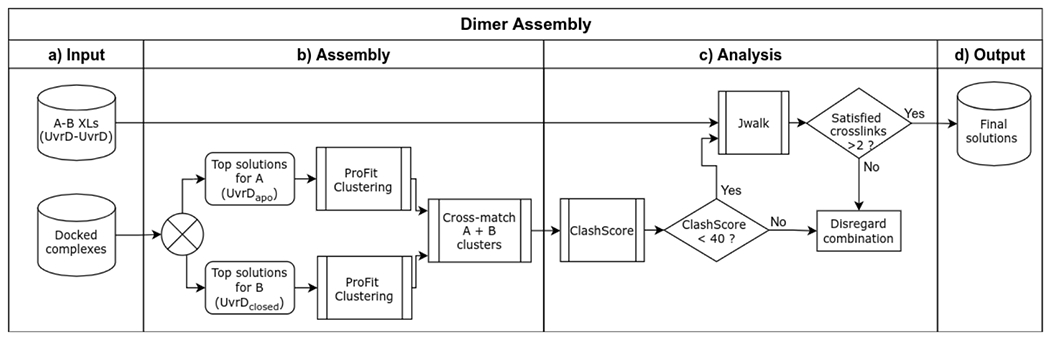
Two monomer models (X and Y), previously and separately docked to a common receptor model (R), are combined to generate receptor-dimer models that satisfy the highest number of crosslinks between the two monomers. a,b, Top docking poses for each monomer (R-X and R-Y) are clustered to eliminate redundancies and accelerate subsequent steps. c, Representative models obtained by clustering each of the two groups are cross-matched to generate combined receptor-dimer coordinate files (R-X-Y), and analyzed for cross-links satisfied between X-Y using Jwalk. d, receptor-dimer models satisfying >2 cross-links are ranked by number and average distance of satisfied X-Y cross-links for further analysis.
