Fig. 4. Global NER fully depends on ongoing transcription and UvrD, but not Mfd.
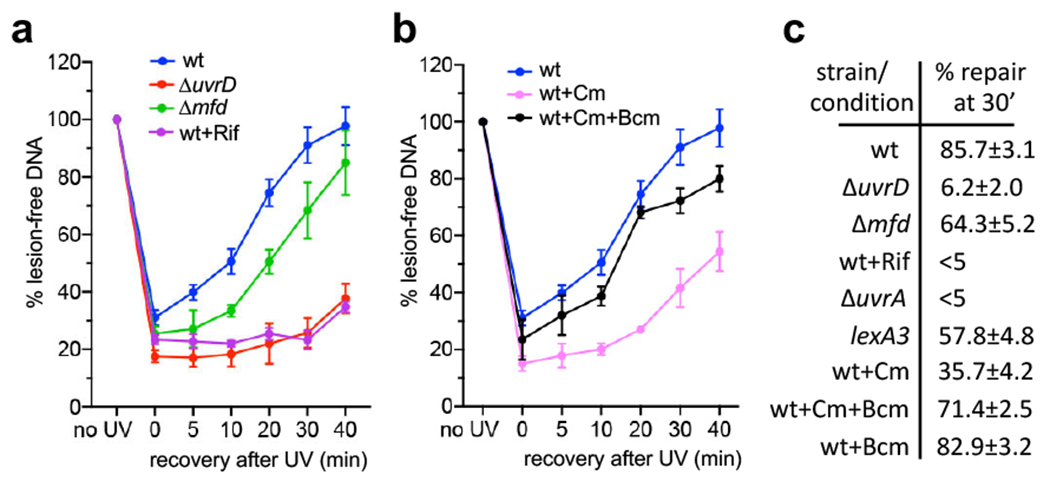
a, Transcriptional shutdown by rifampicin (Rif) abolishes NER. Wild type (wt; blue), ΔuvrD (red), and Δmfd (green) cells were briefly UV irradiated at 50 J/m2 and allowed to recover for the indicated times. Wild type cells were also pretreated with high Rif prior to UV irradiation. Rif did not decrease the cellular level of NER enzymes during the time of the experiment (Extended Data Fig. 10). Genomic DNA was isolated and treated with T4 endonuclease V (T4endoV) at the indicated times, and then resolved on alkali-agarose gels. Representative gels are shown in Extended Data Fig. 8. The percentage of repaired (lesion-free) DNA in T4endoV-treated samples is plotted for each time point relative to the untreated samples. Data are the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. b, Chloramphenicol (Cm) delays NER primarily due to excessive Rho-dependent transcription termination, not due to the translational shutdown per se. Experimental setup is as in (a), except that wt cells were pretreated with Cm (pink) or Cm together with bicyclomycin (Bcm; black) prior to UV irradiation. Genomic DNA was isolated and treated with T4endoV at the indicated times, and then resolved on alkali-agarose gels. Representative gels are shown in Extended Data Fig. 8. The percentage of repaired DNA is plotted for each time point relative to the untreated samples. Data are the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. c, Summary of all T4endoV results at the 30 min of a post-UV recovery. Representative gels and DNA repair plots for ΔuvrA and lexA3 mutants are shown in Extended Data Fig. 8. Numbers are the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments.
